- Introduction
- What a Warehouse Management System Does
- Key Components of WMS Automation
- Steps to Automate a Warehouse Management System
- How Automation Improves Warehouse Functions
- Real-World Examples of WMS Automation
- GXO Logistics: A 3PL Success Story
- Challenges in WMS Automation
- Best Practices for Successful Automation
- Future of Warehouse Management System Automation
- Unlocking Growth Through Warehouse Management System Automation
- Frequently Asked Questions
Table of Contents
How Warehouse Management System Automation Works
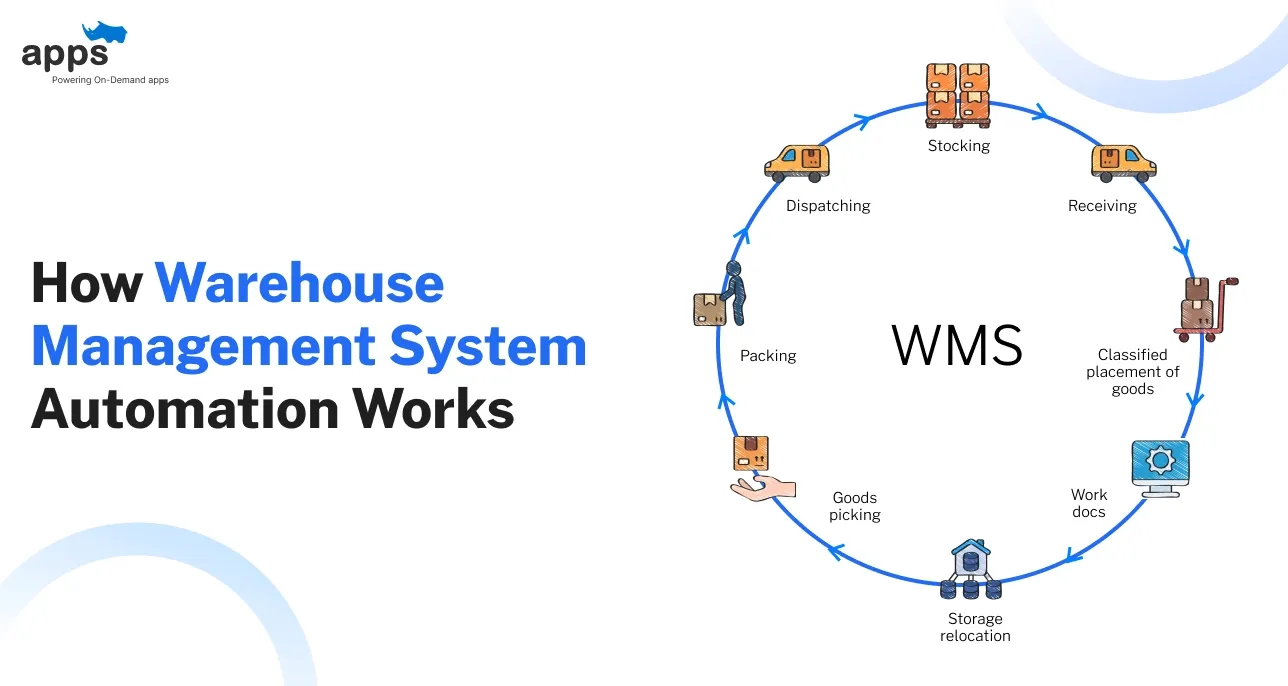
Introduction
Warehouse management system automation is transforming logistics across industries.
From e-commerce hubs to hospital supply chains, companies are adopting automation to boost accuracy, cut costs, and meet rising demand. Surging online sales and labor shortages have accelerated this shift.
While exact global adoption rates are unclear, the trend is unmistakable: 89% of organizations surveyed plan to utilize modernized Warehouse Management Systems for labor planning and management by 2024. (Source: G2)
This guide is built for startup founders, IT leaders, and operations heads exploring automation.
You’ll learn what a warehouse management system (WMS) does, the core technologies involved, and the step-by-step path to implementing automation.
We'll also cover benefits, real-world case studies, key challenges, and future trends—everything you need to understand how warehouse management system automation works and why now is the right time to start.
What a Warehouse Management System Does
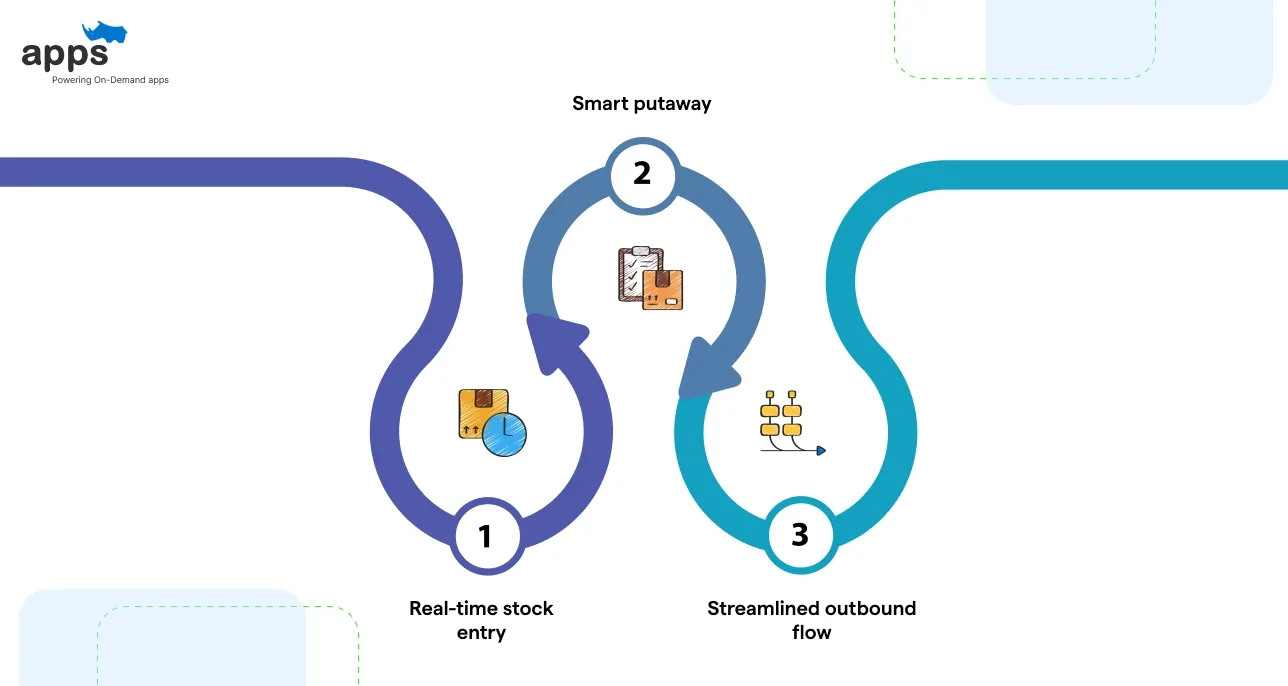
A modern warehouse management system automation setup does more than replace paperwork. It brings intelligence and speed to every touchpoint of the warehouse.
Here’s how it works in practice:
- Real-time stock entry: Warehouse staff use barcode scanners or RFID readers instead of manually jotting down receipts. This enables instant updates to inventory levels.
- Smart putaway: The system then instructs staff — or robots — to place items in the most efficient storage locations, based on item demand and category.
- Streamlined outbound flow: It auto-generates picking lists, validates packing, and updates shipping data. All steps are tracked in real time.
These are not isolated tasks. Warehouse management system automation links them into a single, intelligent loop.
And when your WMS is integrated with an ERP, data flows smoothly across procurement, inventory, and delivery functions.
This level of warehouse management automation transforms a warehouse from a reactive space into a proactive, self-adjusting system.
Key Components of WMS Automation
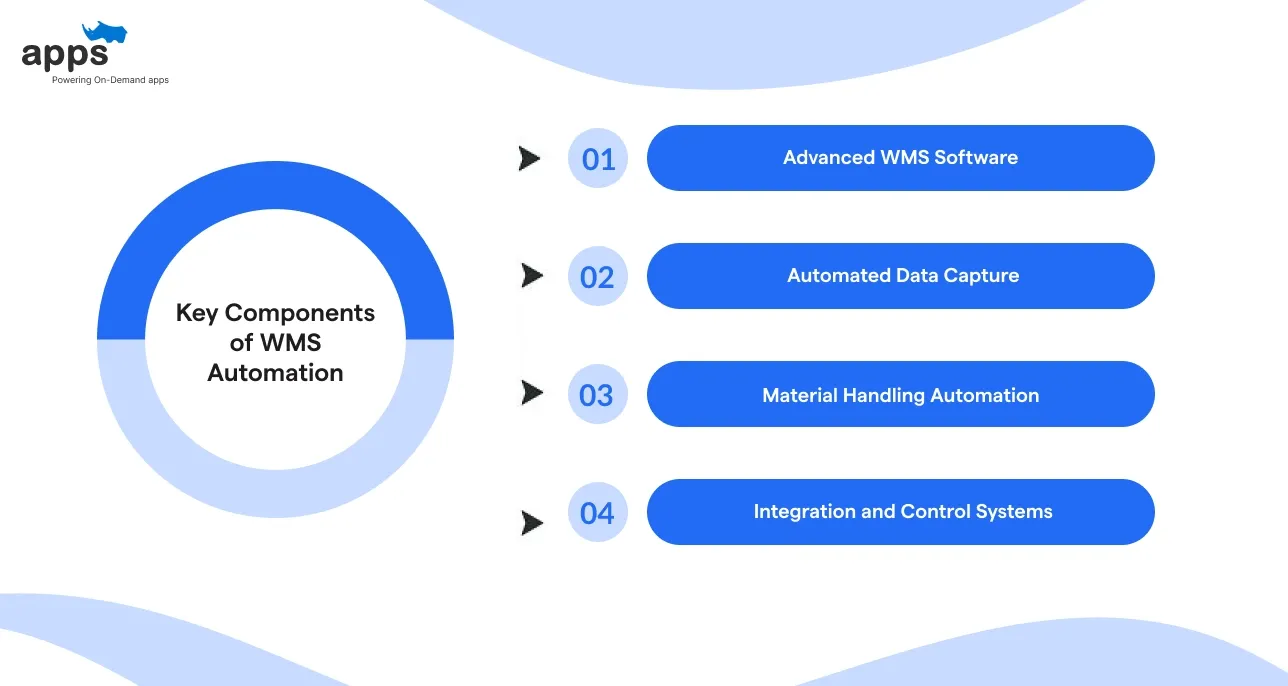
Implementing warehouse management system automation requires software, hardware, and process improvements working in sync.
A truly automated WMS environment typically involves several key components working together to handle tasks with minimal human intervention.
Below, we outline the significant components of warehouse management automation:
A) Advanced WMS Software
At the core is a robust WMS platform configured for automation. It should support real-time inventory updates, rule-based process flows, and integration with automated equipment.
The WMS acts as the central command, issuing tasks to robots or workers and optimizing decisions like where to store an item or which order to pick next.
Modern WMS solutions often include analytics and AI features to streamline operations further.
B) Automated Data Capture
Technologies like barcode scanners, RFID tags, and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors are essential for warehouse management system automation. These tools automatically identify products and record movements without manual data entry.
For instance, RFID gates can register inventory as it passes through receiving, and handheld or wearable barcode scanners speed up picking with accurate scans.
Automated data capture provides the real-time inputs the WMS software needs to make quick decisions.
C) Material Handling Automation
Physical automation equipment is a visible component of warehouse management automation. This includes conveyor systems, sortation machines, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS).
Such equipment moves goods through the warehouse, retrieves pallets or totes, transports items to picking stations, sorts packages, and more, according to instructions from the WMS.
For example, an AS/RS can automatically shuttle bins of products to a picker or packing station on demand. These technologies handle the heavy lifting and repetitive travel humans would otherwise do.
D) Integration and Control Systems
To tie everything together, warehouses often use integration middleware or a warehouse control system (WCS). This software layer links the WMS with the automation equipment on the floor.
Seamless integration is critical. The warehouse management system automation capabilities depend on all components speaking the same language. Additionally, integration with external systems like ERP, shipping carriers, or customer platforms enables end-to-end automation beyond the warehouse’s four walls.
When these components operate harmoniously, the result is a highly automated warehouse.
For instance, imagine an incoming pallet arriving: a sensor automatically notifies the WMS, which creates a put-away task.
An AGV then ferries the pallet to a storage location directed by the system. Later, when an order is placed, the WMS triggers an AS/RS to retrieve the item, a conveyor routes it to packing, and a shipping label is printed automatically — all with minimal manual touches.
Achieving this synergy between software intelligence and automated machinery is the essence of warehouse management system automation.
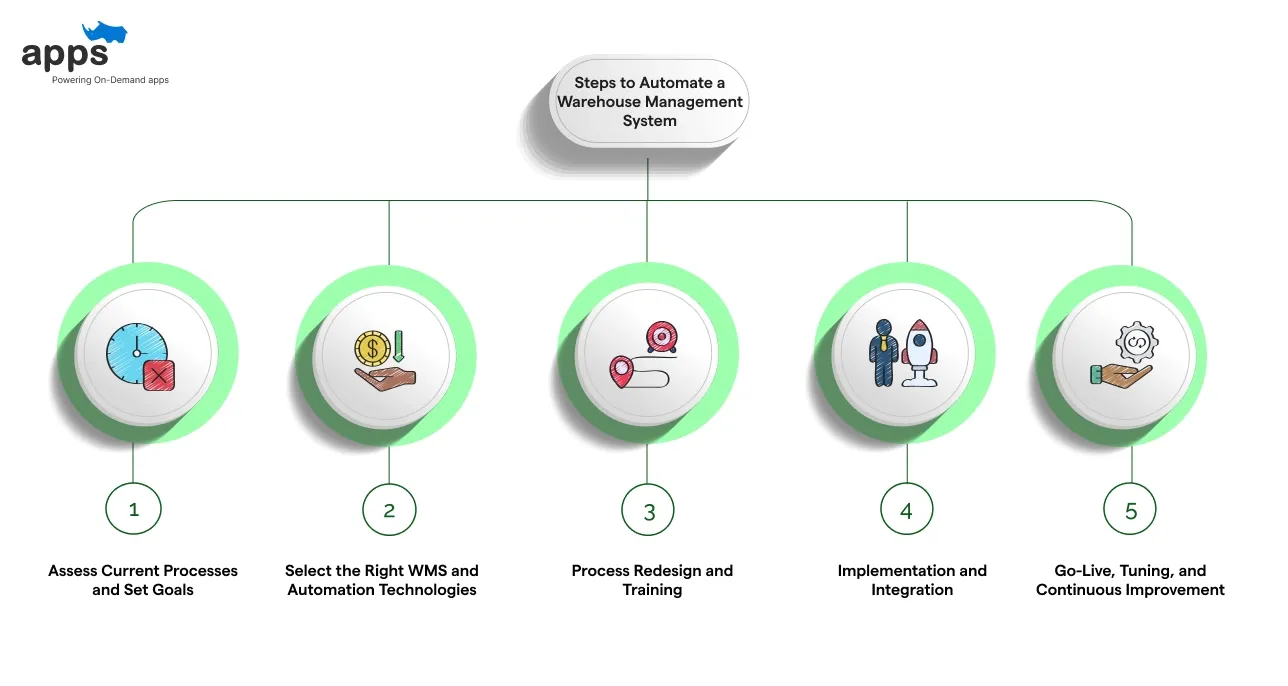
Steps to Automate a Warehouse Management System
Automating your warehouse is more than a tech upgrade. Each phase, from planning to deployment, demands clarity, precision, and team alignment. Here's how to approach warehouse management system automation the right way.
Below are the five key steps that form a practical roadmap to implement automation effectively.
Step 1: Assess Current Processes and Set Goals
Begin by conducting a thorough review of existing operations. Look for pain points such as inventory inaccuracies, order delays, or inefficient picking routes. Define measurable goals.
For example, reducing order cycle time by 40% or achieving 99% inventory accuracy.
This analysis will form the basis for justifying automation investments. Estimating your expected return on investment (ROI) is essential, so you can benchmark results as your warehouse management system automation progresses.
Step 2: Select the Right WMS and Automation Technologies
With goals established, evaluate tools that align with your objectives. You might upgrade to a more automation-ready WMS or enhance your current setup with compatible modules.
Ensure your chosen platform integrates easily with automation tools like barcode systems, conveyors, AGVs, or picking robots.
Scalability is key. Cloud-based WMS platforms with mobile scanner support offer a cost-effective entry point.
To enable complete warehouse management automation, your WMS, WCS, and devices must communicate effortlessly and adapt to evolving warehouse demands.
Step 3: Process Redesign and Training
Before deploying technology, map new workflows. Identify where automation will replace manual steps and how roles will shift.
For example, change your landscape from walking aisles to managing robotic workflows. Optimize layout by creating dedicated zones for conveyors, picking stations, or automated sorters.
Equally critical is staff training. Everyone from operators to IT personnel should understand how to use and monitor the new WMS.
Practical training ensures the system is appropriately used and reduces downtime. Successful warehouse management system automation hinges on proactive change management and staff alignment.
Step 4: Implementation and Integration
Now comes the deployment phase. Install and configure your WMS with scanners, sensors, and automated systems.
Consider a phased approach to reduce disruption, like automating one process (like receiving) or warehouse zone at a time.
Focus on seamless system communication. Connect devices to the WMS, link control software, and integrate your ERP or e-commerce platform. Test everything in a simulated environment using live data.
Fix configuration or communication errors before going live to avoid cascading issues during full rollout.
Step 5: Go-Live, Tuning, and Continuous Improvement
Once testing is complete, roll out automation gradually across all operations. Closely monitor system performance.
Adjust as needed, such as refining conveyor speed, optimizing pick path logic, or re-slotting products for better flow.
Use WMS dashboards to analyze performance indicators like lines picked per hour or order accuracy. Continuous feedback loops will reveal what works and what needs improvement.
Remember, warehouse management system automation is not a one-time project. It is an evolving initiative that must be fine-tuned and maintained to keep delivering value.
Following this structured five-step approach ensures a smooth transition. It accounts for technology implementation and human adaptation, creating the foundation for sustainable warehouse management automation success.
How Automation Improves Warehouse Functions
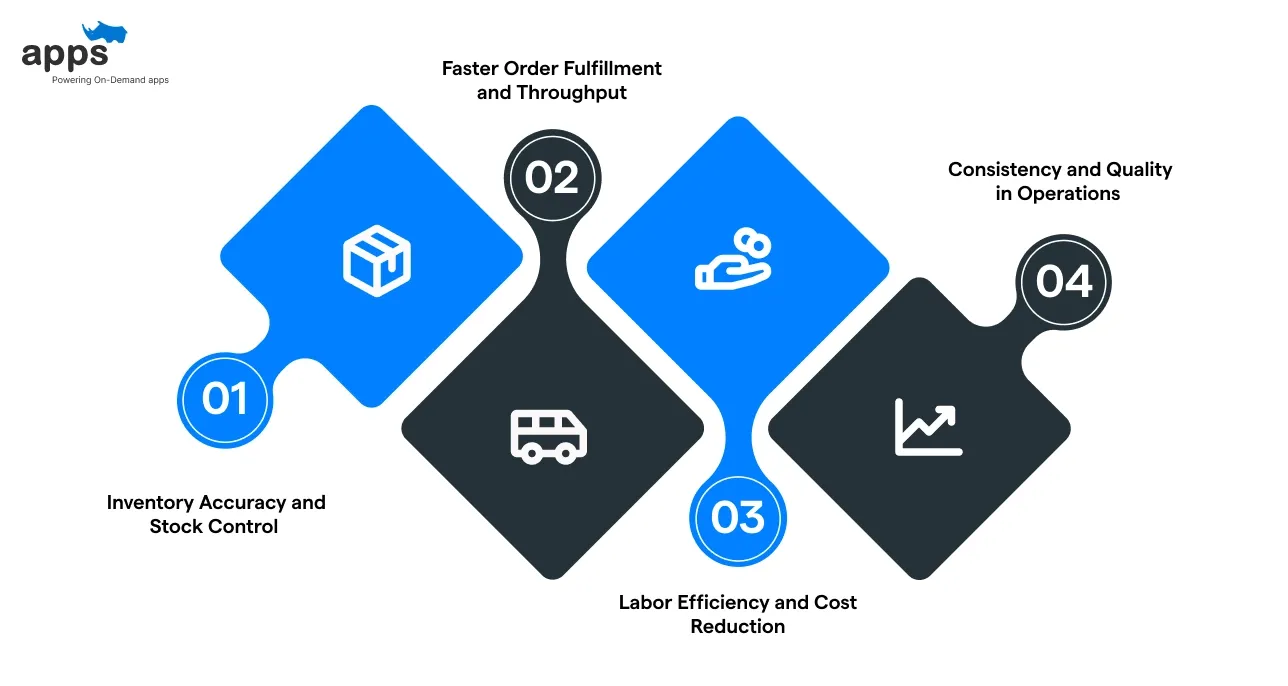
Automating a warehouse management system can significantly improve virtually all warehouse functions.
By minimizing manual work and human error, warehouse management system automation enables warehouses to operate more efficiently, accurately, and quickly. Here are some of the key ways automation enhances warehouse performance.
A) Inventory Accuracy and Stock Control
Inventory is the heartbeat of your warehouse. If it’s inaccurate, everything else, like picking, packing, and shipping, will feel the consequences.
- Real-Time Precision with Automation
Automation significantly improves inventory tracking accuracy. Barcode scanners, RFID tags, and real-time data updates eliminate errors that arise from manual entries.
The warehouse management system captures every item movement automatically, ensuring up-to-date records.
- The Impact on Accuracy and Stock Visibility
Automated facilities are far more likely to achieve near-perfect inventory accuracy. In fact, according to a survey by Robotics Business Review,
‘Automated warehouses are 76% more likely to increase inventory accuracy to 99% or higher and 40% more likely to ship orders within one day of being placed.’
This precision reduces stockouts, improves order fill rates, and supports reliable reordering. Warehouse management automation virtually eliminates the inventory mistakes that plague manually run facilities.
B) Faster Order Fulfillment and Throughput
Speed is a competitive advantage. The faster you fulfill orders, the happier your customers are and the more orders you can take.
- Parallel Task Execution with Smart Systems
Automation allows tasks that were once sequential to co-occur.
Robots can pick multiple orders in parallel while conveyors transport others for packing. This creates a streamlined, overlapping process that boosts overall speed.
- Better Delivery Performance
Studies show that best-in-class automated operations average under 7 hours from order placement to shipment.
These improvements aren’t limited to large operations. Automation eliminates unnecessary steps, minimizes walking distance for human pickers, and ensures direct routing via conveyors or bots.
With warehouse management system automation, orders leave the facility faster, leading to higher customer satisfaction and long-term retention.
C) Labor Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Labor is one of the highest ongoing costs in any warehouse. Automating key workflows reduces dependency on manual labor and lowers the overall cost per order.
- Doing More with Fewer Hands
Labor efficiency is one of the most immediate benefits of warehouse management system automation.
Machines handle repetitive and physically intense tasks, freeing up workers for roles that require oversight or decision-making.
- Measurable Cost Savings and Workforce Flexibility
According to industry benchmarks, automated warehouses reduce labor costs by around 3% annually.
Over time, this results in a 36% cumulative improvement, especially when compared to manual operations. (Source: Cyngn)
Automation also addresses labor shortages. Scaling output helps avoid excessive overtime without requiring more staff in peak seasons. Safety improves, too, as robots take over high-reach or heavy lifting tasks, reducing injuries and fatigue.
In these environments, a smaller workforce becomes exponentially more productive when supported by warehouse management automation.
D) Consistency and Quality in Operations
Consistency is hard to maintain with a human-only workforce. Automation brings the discipline, speed, and standardization your warehouse needs.
- Reliability Without Fatigue or Variance
Machines operate with a level of consistency humans cannot match whether early morning or midnight, automation executes with the same precision every time.
This reliability directly translates to better service levels.
- Fewer Errors and Higher Customer Satisfaction
Automated sorters, pick-to-light systems, and guided workflows reduce fulfillment errors. Packages are sorted correctly.
The correct item is picked on the first try. Returns and complaints decrease.
High-performing companies that rely on warehouse management system automation often see better revenue growth, as consistent service quality builds stronger customer loyalty.
Real-World Examples of WMS Automation
Exploring real-world warehouse management system automation applications shows how industry leaders use technology to boost speed, accuracy, and scalability across operations.
A) Amazon’s Robotic Fulfillment Centers
Amazon has transformed its warehouse operations with over 750,000 robots deployed across its fulfillment centers as of 2023.
These mobile units, developed partly from its acquisition of Kiva Systems, work alongside human associates to carry shelves of products to designated picking stations.
The robots are orchestrated by Amazon’s WMS and robotic control system, which precisely manages every movement. According to Amazon Robotics, this integration enables near-perfect inventory accuracy and hyper-efficient order processing, fueling services like same-day delivery in many cities.
This warehouse management system automation scale powers Amazon’s industry-leading fulfillment speed.
B) Walmart’s Inventory Management Automation
Walmart deployed a cloud-based WMS backed by AI to manage its vast retail and distribution ecosystem. The system enables real-time inventory visibility across thousands of locations.
It integrates with mobile scanners used by store staff and autonomous shelf-scanning robots, which monitor stock levels after hours.
As reported by SupplyChain247, Walmart uses this automation to reduce excess inventory, hit target in-stock levels, and fulfill online orders with speed and accuracy, making it a prime example of omnichannel warehouse management automation.
C) Ocado’s Automated Grocery Warehouses
UK-based online grocer Ocado operates some of the most highly automated grocery fulfillment centers globally.
In these facilities, thousands of robots traverse a grid-based system, carrying bins of goods to human pickers.
This process is managed by Ocado’s custom-built WMS and control systems, which use AI to optimize travel paths, reduce congestion, and anticipate demand.
This warehouse management system automation level allows Ocado to fulfill tens of thousands of orders per week with a lean human workforce, and their technology is now licensed to grocers worldwide.
GXO Logistics: A 3PL Success Story
Leading third-party logistics provider GXO Logistics uses warehouse management system automation to increase throughput and support retailers with high-volume needs.
Collaborative robots (cobots) deliver goods to packers in their facilities, while autonomous forklifts handle pallet movements.
GXO’s AI-powered WMS manages this automation, coordinating inventory, labor, and robotics in real time.
For one retail client, the system improved order processing speeds by over 200% while significantly lowering error rates, proving that warehouse management automation is scalable for 3PLs, not just enterprise giants.
Challenges in WMS Automation
While the benefits of automation are compelling, implementing warehouse management system automation comes with real-world hurdles. Organizations often face several obstacles, from financial concerns to integration issues when transitioning from manual to automated systems.
Here are the four most common challenges in warehouse management automation and how they affect adoption.
A) High Initial Costs and ROI Concerns
Upfront costs can derail automation before it even begins. From hardware to integration, the investment is significant, and the ROI isn’t always immediate.
- Automation Demands Major Upfront Investment
One of the most significant barriers is cost.
Purchasing WMS licenses, robotics, sensors, conveyor systems, and upgrading infrastructure can cost millions for a large facility. Even smaller operations find automation setups financially demanding.
According to Cyngn, nearly one-third of companies report that budget constraints are the top obstacle to adopting warehouse robots. Even after deployment, ROI may take 2 to 3 years on average to materialize.
- The ROI Doubt Factor
Organizations worry about fluctuating order volumes and margins.
What if the automation doesn’t pay off quickly? This leads to hesitation, especially among risk-averse stakeholders. Projects often need strong C-suite backing and detailed ROI forecasting to get off the ground.
For this reason, companies are increasingly opting for phased rollouts or pilot projects, which provide short-term gains and justify broader investment.
B) Integration Complexity
Most warehouses run a combination of legacy and modern systems. Getting them all to work together during automation is no small feat.
- More Devices = More Data = More Complexity
Every warehouse management system automation initiative introduces new physical and digital moving parts.
Robots, scanners, IoT sensors, and conveyors must communicate with the WMS, WCS, ERP, and possibly third-party platforms.
If even one system fails to sync, warehouse flow can halt.
- Legacy Systems Create Bottlenecks
Many older warehouses still run on outdated software that was not built to integrate with modern automation. This makes real-time syncing difficult, often requiring middleware or costly workarounds.
SupplyChainBrain highlights that poor integration planning is a significant reason automation rollouts stall or underperform.
Organizations are increasingly turning to modular, open-architecture systems that are easier to connect and scale to address this.
C) Change Management and Workforce Adaptation
Tech gets the spotlight, but human adaptability determines success. Employees must be aligned, supported, and involved early in the automation journey.
- Automation Is Not Just Tech — It’s Cultural
Deploying automation is often more of a people challenge than a tech one. Employees doing things manually for years may resist new systems, fearing replacement or complexity.
Without clear communication and training, morale can suffer.
- Training and Communication Are Crucial
Employees must learn to interact with the WMS, use barcode scanners or tablets, and work alongside robots. If that learning curve isn’t addressed, productivity may dip, and automation may be underutilized or sabotaged.
Forbes stresses that workforce resistance is one of the top causes of failed automation projects. Solutions include proactive training, role redefinition, and involving staff early so they feel like contributors, not casualties.
Ultimately, warehouse management automation only works when your people and machines work together.
- Scalability and Future-Proofing
Warehouses aren’t static. Systems that work today may crumble under tomorrow’s demands if they can’t adapt and evolve.
- Today’s Tech May Not Fit Tomorrow’s Needs
One of the hidden risks in automation is locking into a rigid system. What works for your current volume or warehouse layout may not scale if orders double or your business model evolves.
Decision-makers fear investing in tools that could soon be obsolete.
- The Market Evolves Rapidly
With drone inventory scans, AI vision systems, and AMRs advancing quickly, choosing the wrong vendor or tech ecosystem today could limit flexibility tomorrow.
According to Modern Materials Handling, companies are urged to prioritize systems supporting updates, new modules, and third-party hardware integration.
A well-designed warehouse management system automation strategy should not only meet current needs, but also grow and adapt with your operations.
Best Practices for Successful Automation
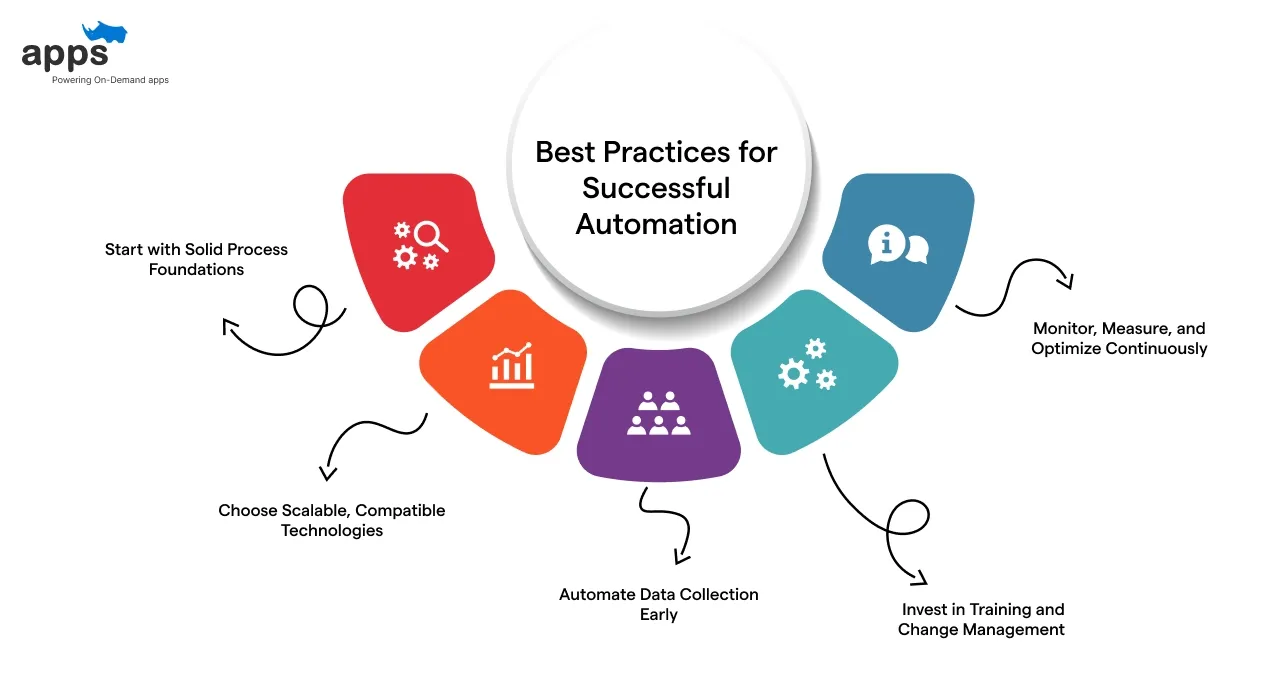
Implementation alone isn't enough to get the most out of warehouse management system automation. Success depends on smart choices before, during, and after automation begins.
Below are five proven best practices every warehouse team should follow.
1) Start with Solid Process Foundations
Before jumping into automation, fix the basics. A broken process won’t magically improve just because it’s faster.
Here’s what to keep in mind
- Standardize workflows like receiving, put-away, picking, and counting
- Eliminate bottlenecks manually so that automation has a clean slate
- Clean your data — inaccurate SKUs and inventory logs will destroy system accuracy.
A good rule? If it doesn’t work well without automation, it won’t work better with it. Start small, refine manually, then scale with confidence.
2) Choose Scalable, Compatible Technologies
Your warehouse won’t look the same in 3 years. Your tech shouldn’t feel outdated either.
Here’s what to keep in mind
- Avoid vendor lock-in with systems that don’t support open integration
- Invest in cloud-based WMS platforms that allow modular growth.
- Ask scalability questions — can this solution grow 10x without a rebuild?
Warehouse management automation should grow with your operation, not limit it.
3) Automate Data Collection Early
Before adding robots, add trust to your data. The best automation still fails with bad input.
Here’s what to keep in mind
- Start with barcode scanners or RFID to track inventory in real time
- Use cloud WMS for centralized, always-updated data access
- Eliminate human error in data entry wherever possible
Once your team can trust every number, every scan, and every alert, your warehouse management system automation has absolute power.
4) Invest in Training and Change Management
No automation effort succeeds without your people. Training isn’t a phase — it’s part of the foundation.
Here’s what to keep in mind
- Train beyond the screen — explain how roles and workflows will evolve
- Address job security fears — show that automation enhances, not replaces
- Create peer champions — assign “super users” to lead change on the ground.
Want success? Make automation a team initiative, not a tech project.
5) Monitor, Measure, and Optimize Continuously
Automation isn’t set-it-and-forget-it. Your warehouse is alive — treat it that way.
Here’s what to keep in mind
- Set up WMS dashboards to track picker speed, equipment use, and order flow
- Run performance reviews regularly and tweak workflows as needed
- Schedule preventive maintenance before machines force you to
Companies that succeed with warehouse management automation never stop optimizing. The goal? Constant improvement, not one-time efficiency.
The bottom line: These best practices help you avoid costly mistakes and set your WMS automation up for accurate, repeatable results.
Future of Warehouse Management System Automation
AI, robotics, and real-time data will shape the next phase of warehouse management system automation. Future WMS platforms will dynamically optimize inventory layouts and predict demand using machine learning.
Automation is also scaling rapidly. According to Modern Materials Handling, 75% of companies will adopt cyber-physical automation by 2027.
- Picking robots with computer vision
- Drones for inventory checks
- Autonomous trucks and IoT sensors
- 5 G-powered real-time coordination
“Dark warehouses” (fully automated, no lighting needed) and micro-fulfillment centers are also emerging, especially in urban grocery logistics. Sustainability is another driver: Greener robots and energy-efficient systems are becoming the new standard.
Today, businesses investing in warehouse management automation are positioning themselves to lead in tomorrow’s logistics landscape.
Unlocking Growth Through Warehouse Management System Automation
Warehouse management system automation is no longer optional; it’s becoming the new baseline for scalable, efficient operations. From inventory tracking to fulfillment, automation reduces costs, boosts speed, and improves accuracy.
Success lies in aligning people, processes, and platforms. Companies that plan thoroughly and choose the right tools gain faster ROI and long-term resilience. Automation unlocks operational excellence and sets the foundation for sustainable growth.
Platforms like AppsRhino offer custom Warehouse Management System Automations and mobile automation solutions. With the right tech partners, your automation journey is not just achievable — it’s transformational.
From streamlining inventory to empowering on-the-go operations, your transformation starts here. Don’t adapt. Lead. Automate with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the three levels of warehouse automation?
The three levels are basic automation (barcode scanning), system automation (Warehouse Management system automation integration), and full warehouse management system automation involving robotics, AI, and IoT to streamline all warehouse operations.
2. What are the four types of warehouse management systems?
The four Warehouse Management system automation types include standalone systems, ERP modules, cloud-based Warehouse Management systems, and integrated platforms with warehouse management system automation features for inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and real-time warehouse visibility.
3. What technology is used in warehouse management?
Technologies used include barcode scanners, RFID, IoT sensors, cloud platforms, and robotic systems — all essential for achieving efficient warehouse management automation in modern supply chain and logistics operations.
4. What is the warehouse technology in 2025?
In 2025, warehouse technology includes AI-driven robotics, drone inventory checks, 5 G-enabled systems, and advanced warehouse management system automation that supports real-time coordination between humans, machines, and data.
5. What is WMS automation?
Warehouse Management system automation uses software, hardware, and real-time data to automate tasks like inventory updates, order routing, and tracking. It’s the foundation of scalable warehouse management automation.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What a Warehouse Management System Does
- Key Components of WMS Automation
- Steps to Automate a Warehouse Management System
- How Automation Improves Warehouse Functions
- Real-World Examples of WMS Automation
- GXO Logistics: A 3PL Success Story
- Challenges in WMS Automation
- Best Practices for Successful Automation
- Future of Warehouse Management System Automation
- Unlocking Growth Through Warehouse Management System Automation
- Frequently Asked Questions


