- What is Telemedicine?
- How to Set Up a Telemedicine System?
- What are the roles of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
- What are the Important Benefits of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
- What are the Challenges of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
- Technologies Used in Telemedicine in Healthcare
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Telemedicine
- Future of Telemedicine in Healthcare
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Table of Contents
What is the importance of telemedicine in healthcare?
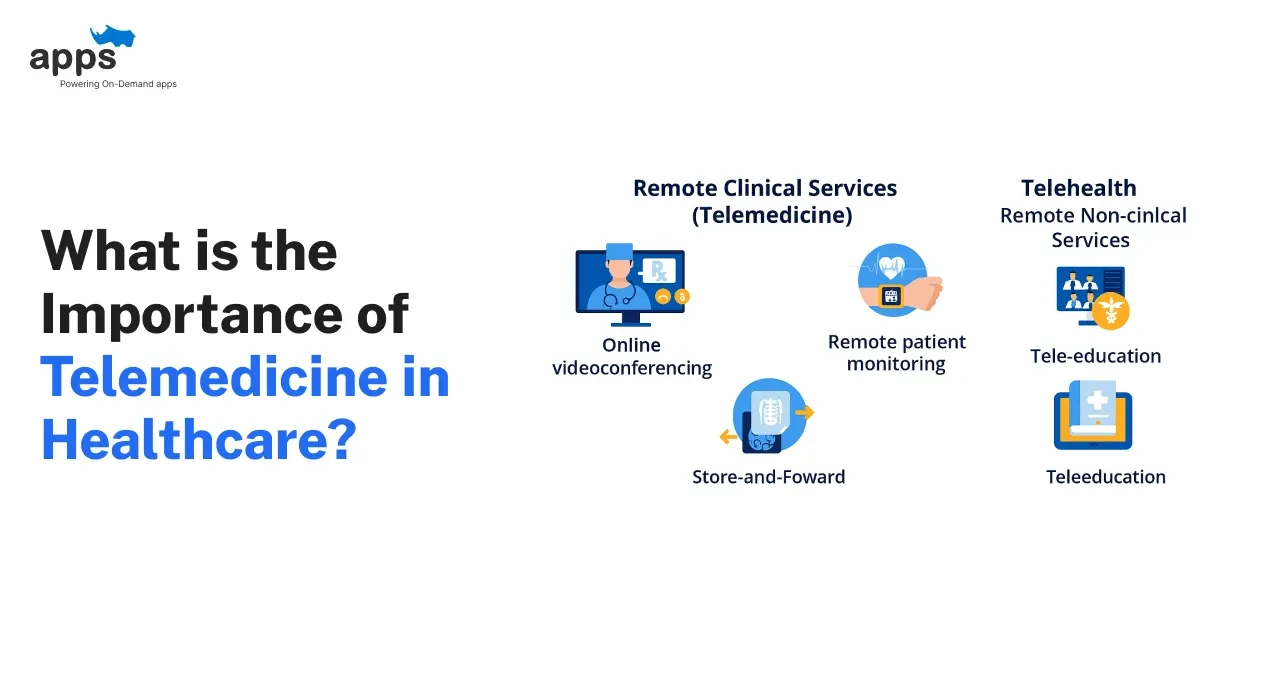
Telemedicine was once considered a niche service, but today, it’s a lifeline for millions.
In fact, telemedicine usage skyrocketed by over 154% during the pandemic, underscoring the increasing importance of telemedicine in healthcare.
Now, it’s not just about convenience, it’s about making healthcare more accessible, affordable, and efficient. As the world continues to face challenges, the importance of Telemedicine in healthcare has never been more apparent.
From reducing costs to expanding access, this technology is transforming the way we receive care. And it’s only getting started.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at how telemedicine is transforming healthcare and explore its role in improving access and outcomes.
First, let’s take a closer look at what telemedicine actually is.
What is Telemedicine?
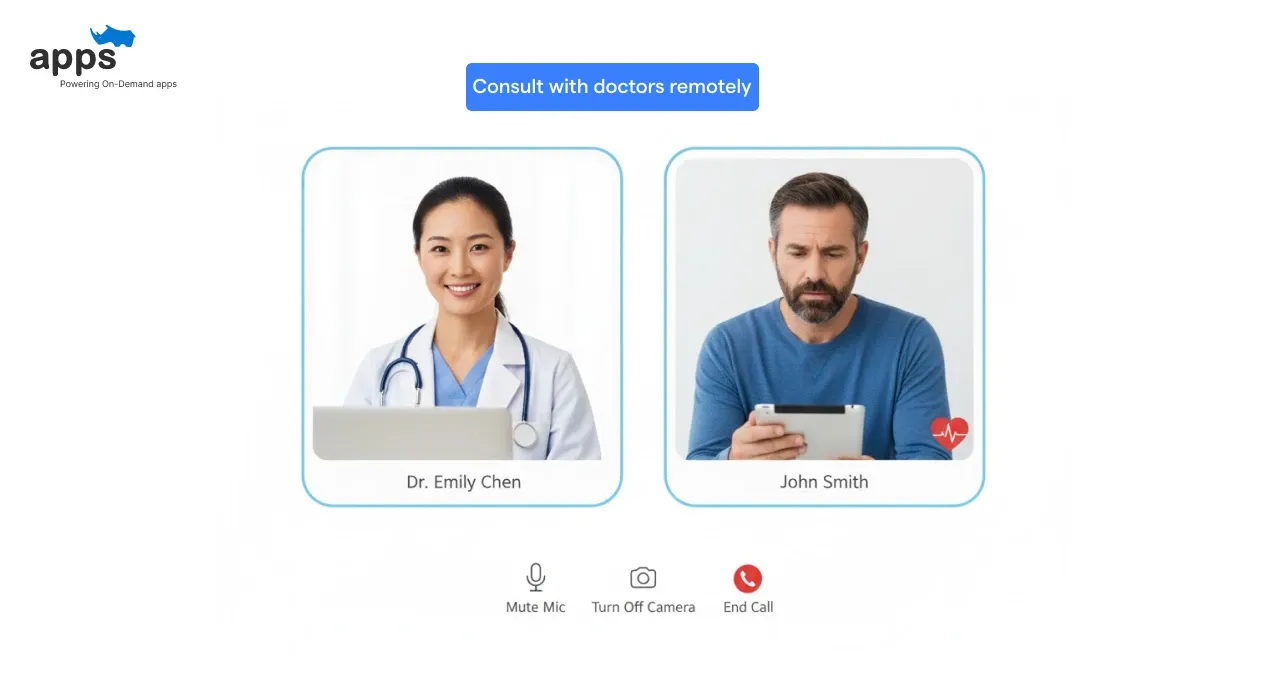
Telemedicine is transforming the way healthcare is delivered, enabling patients to consult with doctors remotely. Using technology, it connects patients and healthcare providers without the need for in-person visits.
It’s making healthcare more accessible and efficient, especially for those facing barriers like location, time, or mobility.
The importance of telemedicine in healthcare has grown rapidly, particularly in reaching underserved communities and improving chronic disease management.
Types of Telemedicine
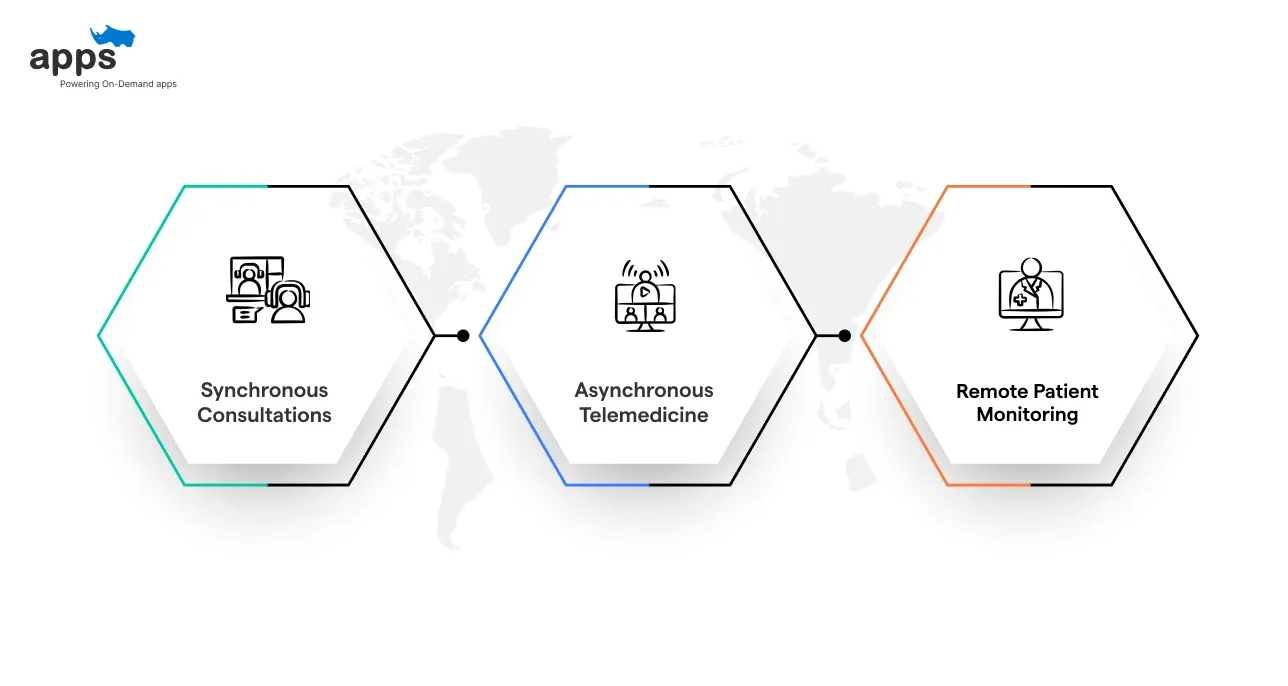
Telemedicine isn’t just one thing. It’s a broad set of tools tailored to meet different healthcare needs:
- Synchronous Consultations: Through video or phone calls, patients can consult doctors for non-emergency issues. It’s a convenient way to get advice on conditions that don’t require an in-person exam.
- Asynchronous Telemedicine: Patient data, such as medical images or lab results, is transmitted to a provider for review. This is commonly used in fields such as dermatology, radiology, and pathology.
- Remote Patient Monitoring: This enables healthcare providers to monitor patient conditions in real-time using devices such as wearables. It’s beneficial for managing chronic conditions like diabetes or heart disease, minimizing the need for frequent in-office visits.
Telehealth vs Telemedicine
Telemedicine and Telehealth might sound like the same thing. Indeed, telemedicine is a part of Telehealth, but it is primarily focused on healthcare delivery.
Let’s take a quick look at the comparison table of Telehealth vs Telemedicine.
| Aspect | Telemedicine | Telehealth |
| Definition | Remote diagnosis and treatment of patients. | Broader scope, including education and admin tasks. |
| Focus | Direct patient care (e.g., consultations). | Health education, remote monitoring, and admin. |
| Technology | Virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring. | Includes telemedicine, as well as wellness programs and management systems. |
| Examples | - Virtual consultations - Chronic disease management - Mental health therapy | - Health education webinars - Remote wellness programs - Patient management systems |
Telemedicine is reshaping the healthcare landscape, making it more cost-effective and accessible for patients and providers.
In the next section, we’ll explore the importance of telemedicine in healthcare and its growing role in today’s healthcare system.
How to Set Up a Telemedicine System?
Setting up a telemedicine system is essential to harness the importance of telemedicine in healthcare.
Here’s a concise roadmap to get started.
Step 1: Assess Your Needs
- Identify your target patients and healthcare services.
- Determine the types of telemedicine services required, such as chronic disease management or urgent care.
- Evaluate workflow requirements and how digital health platforms will fit into your existing infrastructure.
Step 2: Choose the Right Platform
- Select a digital health platform that is secure, HIPAA-compliant, and scalable.
- Ensure compatibility with Electronic Health Record (EHR) and existing hospital systems.
- Look for features like appointment scheduling, video consultations, and patient messaging.
Step 3: Integrate Technology with Workflow
- Train staff on using telemedicine tools effectively.
- Incorporate remote patient monitoring devices and platforms.
- Align documentation, follow-up processes, and communication channels for a seamless patient experience.
Step 4: Ensure Data Security & Compliance
- Implement encryption and secure storage for patient data.
- Verify adherence to HIPAA, GDPR, and local telemedicine regulations.
- Regularly audit systems to maintain privacy and trust.
Step 5: Pilot, Launch, and Optimize
- Begin with a small pilot program to test system reliability.
- Collect feedback from patients and healthcare providers.
- Monitor key metrics like patient satisfaction, engagement, and care outcomes, then scale gradually.
Successfully implementing this roadmap requires the right technology foundation. Ensure your system is built for the future by seeking the best telemedicine app developers for your business.
What are the roles of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
Telemedicine is no longer a futuristic concept; it is a reality.
In fact, it’s a vital component of modern healthcare. Leveraging technology enables patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely, breaking down barriers related to distance, time, and mobility.
The role of telemedicine in healthcare includes various benefits.
- Expanding Access to Care: It bridges the gap for patients in rural or underserved areas, providing them with timely medical consultations and care.
- Reducing Healthcare Costs: By minimizing the need for in-person visits, telemedicine helps lower travel expenses and reduces hospital readmission rates.
- Improving Patient Engagement: With remote monitoring tools and virtual consultations, patients can actively participate in managing their health.
- Controlling Infectious Illness: Doctors can use virtual appointments to prescreen patients for infectious diseases, such as the flu or COVID-19, which helps prevent the spread of these diseases to others in the clinic or hospital.
- Providing Better Clinical Assessment: Practitioners can see the patient in their own home, which can provide important clues for diagnosis, such as identifying triggers in the home environment with the help of an allergist.
- Enhancing Chronic Disease Management: Telemedicine supports the long-term care of conditions like diabetes and hypertension through continuous remote monitoring and medication reminders, which can lead to improved health outcomes.
- Offering Immediate, Urgent, and Specialty Care: Patients can schedule quicker appointments, sometimes on the same day, and easily connect with specialists who may be located far away, eliminating the need for long travel times.
These roles collectively underscore the importance of telemedicine in healthcare, making it an indispensable tool in today's medical landscape.
What are the Important Benefits of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
Telemedicine is changing the way healthcare is delivered. It not only makes care more accessible but also improves efficiency and reduces costs for both patients and providers.
Key benefits of telemedicine include:
1. Improved Access to Care
Telemedicine dramatically increases access to services, improving equity between rural and urban centers. For instance, in 2021, 37.0% of adults in the U.S. used telemedicine, with utilization increasing with age and education level. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other sources confirm improved access to services and care delivery.
2. Increased Patient Convenience
Patients save valuable time and money by eliminating the need to travel, park, and sit in a waiting room, as noted by Johns Hopkins Medicine report. A 2022 McKinsey report found that 60% of patients found telemedicine more convenient than in-person appointments.
3. Better Chronic Disease Management
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) empowers patients and allows providers to intervene quickly, which is crucial for chronic care. RPM programs for conditions like heart failure have been shown to reduce inpatient admissions and aid the management of chronic conditions, per the American Medical Association (AMA).
4. Reduced Healthcare Costs
Telehealth can significantly lower overall costs by decreasing the use of expensive emergency resources and inpatient care. A study on individuals with heart disease found that using telehealth was associated with a reduction in total medical costs (by −$1814 per person), as reported in CDC Stacks and other reviews of cost savings.
5. Lower Hospital Readmission Rates
Providing follow-up and remote monitoring after discharge is effective for reducing costly and risky readmissions. Studies on telehealth for heart failure patients have specifically shown fewer hospital readmissions in the intervention group.
6. Control of Infectious Spread
Telemedicine acts as a barrier to infection by allowing providers to pre-screen patients and preventing sick individuals from coming into the office. This limits the spread of contagious diseases like COVID-19 and the flu, protecting both patients and staff, as highlighted by Johns Hopkins Medicine.
7. Sustained Quality of Care
Despite the remote setting, many physicians report that quality remains high. In 2021, 76.7% of primary care physicians and 73.1% of medical specialists reported being able to provide a similar quality of care to in-person visits "to some extent or a great extent," according to the CDC National Center for Health Statistics.
Telemedicine is more than just a convenience; it’s a powerful tool that enhances care, reduces disparities, and empowers patients.
To truly realize these benefits, you need a digital platform built for scale, compliance, and clinical insight—a platform like Appsrhino.
In this section, we learned about the benefits. In the next section, we will explore the technologies used in telemedicine that enable these benefits, from wearable devices to digital health platforms.
What are the Challenges of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
While the importance of telemedicine in healthcare is evident, its integration presents several challenges that need to be addressed to ensure effective and equitable care delivery.
1. Technological Barriers
Digital Literacy and Access: Patients and providers in rural and underserved areas often face challenges such as low digital literacy and limited access to reliable internet and modern devices.
Infrastructure Limitations: Inadequate IT infrastructure and device availability can impede the deployment of telemedicine solutions, especially in regions with limited resources.
2. Privacy and Security Concerns
Data Protection: The use of digital platforms for healthcare raises concerns about the confidentiality and security of patient data. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and compliance with regulations like HIPAA is essential to maintain patient trust.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the complex landscape of telemedicine regulations and reimbursement policies across different regions can be challenging, affecting the widespread adoption and integration of telemedicine into standard healthcare practices.
3. Limited Physical Examination
Clinical Assessment: The inability to perform physical exams may lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, particularly in complex cases. This limitation underscores the importance of in-person visits for comprehensive assessments.
4. Regulatory and Reimbursement Issues
Policy Variability: Variations in telemedicine regulations and reimbursement policies across regions can hinder its widespread adoption and integration into standard healthcare practices.
Overcoming these challenges of telemedicine requires collaboration between healthcare providers, policymakers, and tech developers.
Technologies Used in Telemedicine in Healthcare
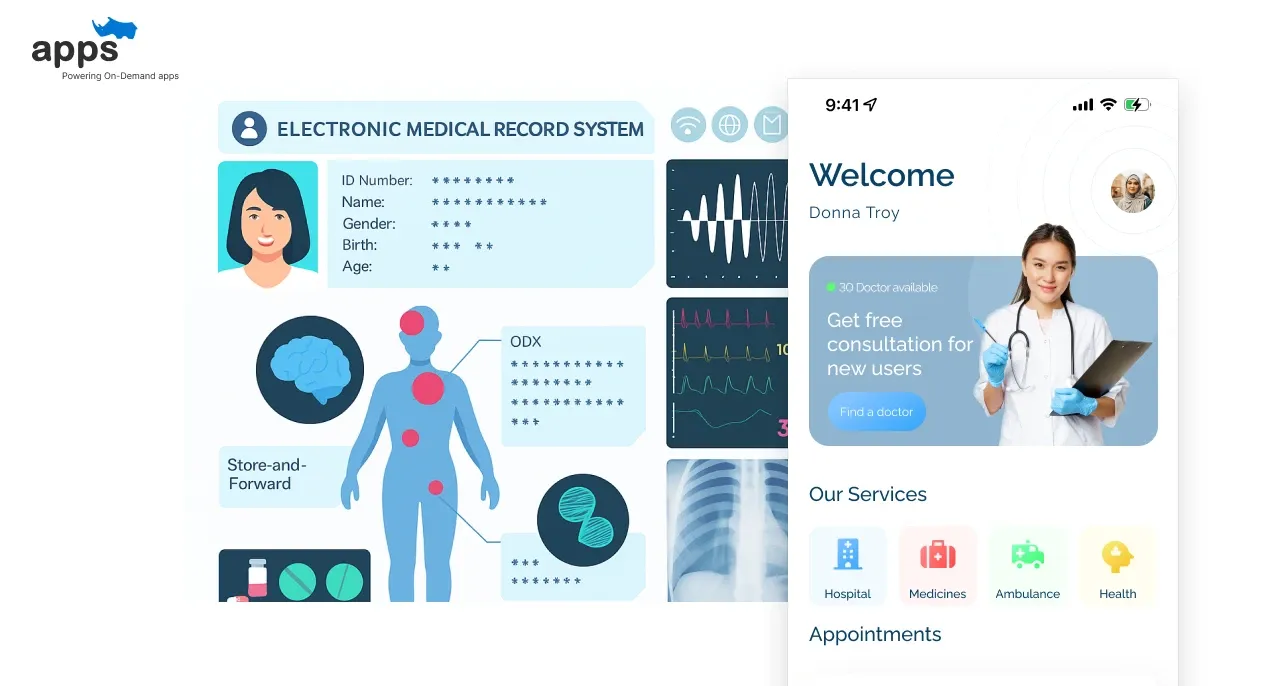
Telemedicine isn’t just about video calls.
It’s powered by technologies that make healthcare faster, safer, and more accessible. From monitoring patients remotely to analyzing data with AI, these tools are reshaping healthcare delivery.
Here’s a look at the key technologies driving telemedicine today.
1. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Devices like wearables and mobile apps track patients’ health in real-time. This is vital for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes or heart disease, allowing timely interventions and reducing hospital visits.
2. Telemedicine Platforms
Platforms enable secure video, chat, or phone consultations. They streamline scheduling, communication, and access to medical records, making care more convenient and efficient.
3. Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration
Linking EHRs with telemedicine ensures doctors have complete patient histories, lab results, and treatment plans at hand. This improves continuity of care and reduces errors.
4. AI and Machine Learning
AI analyzes medical data to assist in diagnosis, predict outcomes, and personalize treatment. It speeds up decision-making and supports healthcare providers with actionable insights.
5. Mobile Health Apps
Apps help patients track symptoms, set medication reminders, and communicate with providers directly. They boost engagement and adherence to care plans.
6. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain keeps patient records secure and tamper-proof. It builds trust in telemedicine while ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Telemedicine technologies are making care more accessible, efficient, and patient-focused.
Next, we’ll explore the advantages and disadvantages of telemedicine to understand its full impact on healthcare.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Telemedicine
Telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, offering numerous benefits while also presenting specific challenges.
Understanding both sides is crucial for optimizing the integration of this technology into healthcare systems.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Reduces travel, hospital visits, and overall healthcare costs. | Hands-on exams are not possible, which may affect diagnosis accuracy. |
| This system enables remote monitoring, improving outcomes and reducing facility burden. | Limited internet or device access can restrict use. |
| Bridges gaps for rural and underserved areas, enhancing healthcare delivery. | Patient data requires strong cybersecurity measures. |
| This approach encourages active health management via virtual consultations and remote monitoring. | Certain conditions require in-person care; remote monitoring may not detect all complications. |
Telemedicine is revolutionizing healthcare delivery, making it more accessible, efficient, and cost-effective.
As we move forward with this blog, it's essential to address the challenges to realize its potential fully.
Future of Telemedicine in Healthcare
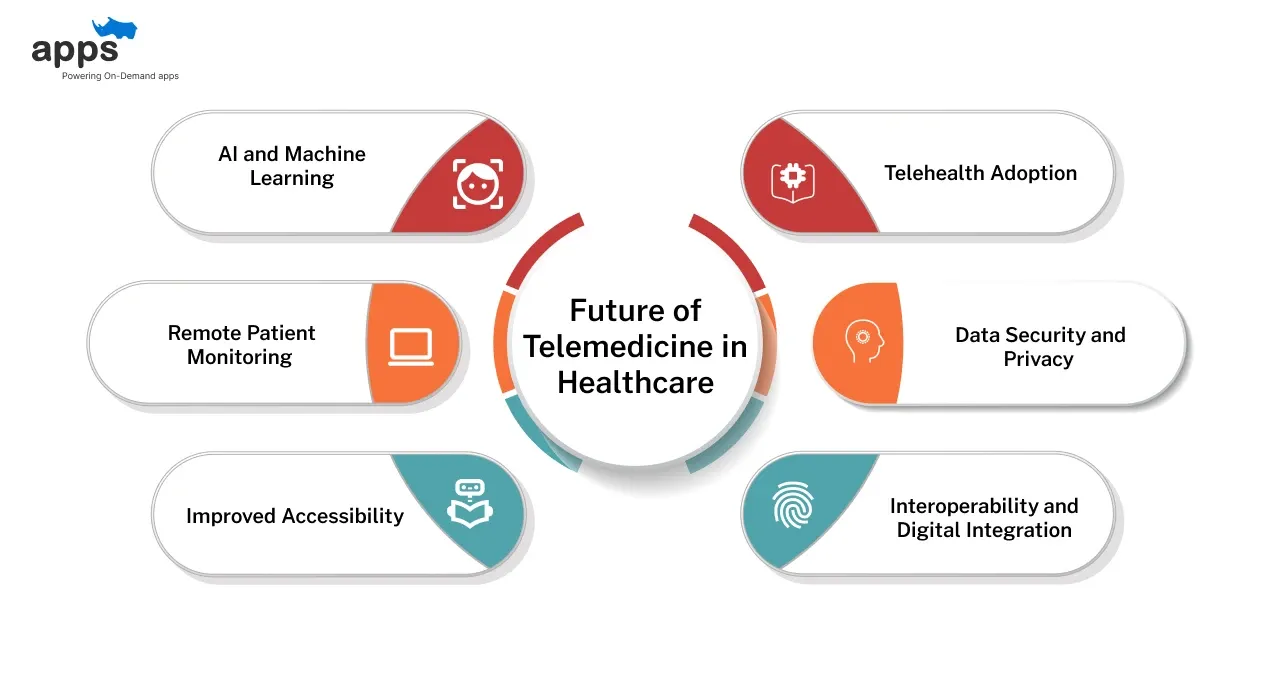
Telemedicine is becoming a cornerstone of modern healthcare.
The importance of telemedicine in healthcare continues to grow as innovations, policies, and digital tools make care more efficient, accessible, and patient-centered.
Here’s what’s shaping the future.
1. AI and Machine Learning: AI analyzes patient data to detect patterns, predict risks, and personalize care. This improves diagnostics, speeds up decisions, and enhances outcomes for patients.
2. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM): Wearables and health apps allow continuous monitoring of chronic conditions. RPM reduces hospital readmissions and enables timely interventions.
3. Improved Accessibility: Telemedicine is expanding into more regions. Initiatives by organizations like the WHO enhance better connectivity, digital literacy, and regulatory support, reducing healthcare disparities.
4. Telehealth Adoption: Remote consultations for minor issues, follow-ups, and chronic disease management are rising. Telehealth reduces travel and waiting times while improving patient convenience.
5. Data Security and Privacy: Secure cloud storage, encryption, and regulatory compliance protect sensitive patient data, fostering trust in telemedicine platforms.
6. Interoperability and Digital Integration: Integrating EHRs, digital health tools, and telemedicine platforms ensures providers have complete, real-time patient data, improving care coordination and clinical decisions.
Telemedicine’s future promises proactive, personalized, and accessible healthcare. These innovations enhance healthcare delivery, reduce costs, and boost patient engagement.
Conclusion: Making the Ultimate Development Decision with Appsrhino
The importance of Telemedicine in healthcare isn’t just a talking point; it’s shaping the future of care.
With tools like remote patient monitoring and virtual consultations, providers can deliver care faster, reduce costs, and reach patients who might otherwise fall through the cracks.
Whether you’re running a small clinic, a growing hospital network, or a telehealth startup, having the right platform makes all the difference.
Appsrhino brings together digital health platforms, EHR integration, and AI-driven insights so you can streamline healthcare delivery and keep patients at the center.
Start by identifying your key telemedicine workflows, then choose a solution that fits your scale, compliance needs, and clinical goals.
If accessibility, efficiency, and smarter patient management matter to you, Appsrhino is built to make it happen.
Why you should choose Appsrhino?
- Real-Time Analytics Dashboard: Instant operational and clinical insights.
- Hybrid No-Code + Custom Code: Mix visual development with advanced custom logic.
- Startup & Enterprise Ready: Solutions fit small clinics and large hospital networks.
- Frictionless Integrations: Integrate CRMs, ERPs, and third-party apps effortlessly.
- AI-Powered Decision Support: Predictive analytics for personalized patient care.
- Secure & Compliant: HIPAA and global healthcare data protection standards.
With Appsrhino, healthcare providers can harness the full role of telemedicine in healthcare, ensuring better chronic disease management, patient engagement, and equitable care delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the three most common types of telemedicine?
The most common types of telemedicine include remote patient monitoring, virtual consultations, and store-and-forward telemedicine, enabling patients and healthcare providers to connect effectively across distances.
What is the role of telemedicine in HIV management?
Telemedicine supports HIV care by enabling continuous monitoring, virtual consultations, and adherence tracking. This improves treatment outcomes, patient engagement, and access to specialized healthcare providers.
What is synchronous and asynchronous telemedicine?
Synchronous telemedicine occurs in real-time through video or phone consultations, while asynchronous telemedicine involves sharing patient data, like images or reports, for later review by healthcare providers.
What are the methods of telehealth delivery?
Telehealth can be delivered via mobile apps, digital health platforms, video calls, secure messaging, and remote monitoring devices, enhancing healthcare delivery and patient access in diverse settings.
How does telemedicine improve chronic disease management
Telemedicine enables remote patient monitoring for chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, allowing healthcare providers to intervene promptly, track progress, and support adherence to treatment plans.
What challenges might healthcare providers face with telemedicine?
Some challenges of telemedicine include technology limitations, patient digital literacy gaps, data security concerns, and integration with existing electronic health records (EHR) and healthcare workflow.
Table of Contents
- What is Telemedicine?
- How to Set Up a Telemedicine System?
- What are the roles of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
- What are the Important Benefits of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
- What are the Challenges of Telemedicine in Healthcare?
- Technologies Used in Telemedicine in Healthcare
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Telemedicine
- Future of Telemedicine in Healthcare
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)


