- What is Costco?
- Understanding the Costco Business Model
- How Does Costco Make Money – Revenue Streams and Cost Structure
- The Costco Business Model Canvas
- Costco vs Walmart Business Model – A Strategic Comparison
- The Ethical and Sustainable Side of Costco’s Business Model
- Costco’s Digital Transformation and E-Commerce Integration
- Key Lessons Businesses Can Learn from the Costco Business Model
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Table of Contents
CostCo Business Model: Strategic Insights

Costco makes billions not by selling more but by charging people to shop.
That single fact turns the usual retail logic upside down, and it works brilliantly.
The Costco business model has redefined how consumers perceive value, loyalty, and trust. Instead of relying on high markups, Costco thrives on a membership model, low-margin strategy, and bulk purchasing power that keeps prices low and customers loyal.
This blog dives into what is Costco’s business model, how it operates behind the scenes, and the key strategies that make it one of the world’s most profitable retailers.
What is Costco?
Costco is a membership-based retail giant that sells products in bulk at low prices.
Instead of relying on big markups, it earns mainly from membership fees and efficient operations.
Its stores are called warehouses, which focus only on essentials:
- No fancy displays
- No unnecessary costs
- Just straightforward value for shoppers
Founded in 1976 as Price Club in California, Costco merged with Costco Wholesale in 1993 and expanded rapidly. Its mission remains clear: to offer quality products at the lowest prices while maintaining strong supplier relationships, as outlined in the Costco Wholesale 2012 mission, business model, and strategy.
With 800+ warehouses across 12 countries, Costco’s warehouse retailing model thrives on bulk sales, low overhead, and consistent pricing.
The no-frills store design keeps operations lean and passes savings directly to members.
Costco’s wholesale strategy combines scale and customer loyalty. By buying in huge volumes, it secures better supplier rates and sells in bulk to members worldwide, delivering consistent value across every location.
Costco’s success comes from keeping things simple, fewer frills, more value.
Next, we’ll uncover the Costco Business Model that powers this global success.
Understanding the Costco Business Model
The Costco Business Model is built on delivering low prices through bulk scale, creating loyalty through membership, and running ultra-efficient operations.
Each central pillar supports the others. The result: a retail giant that remains calm, even when competitors heat up.
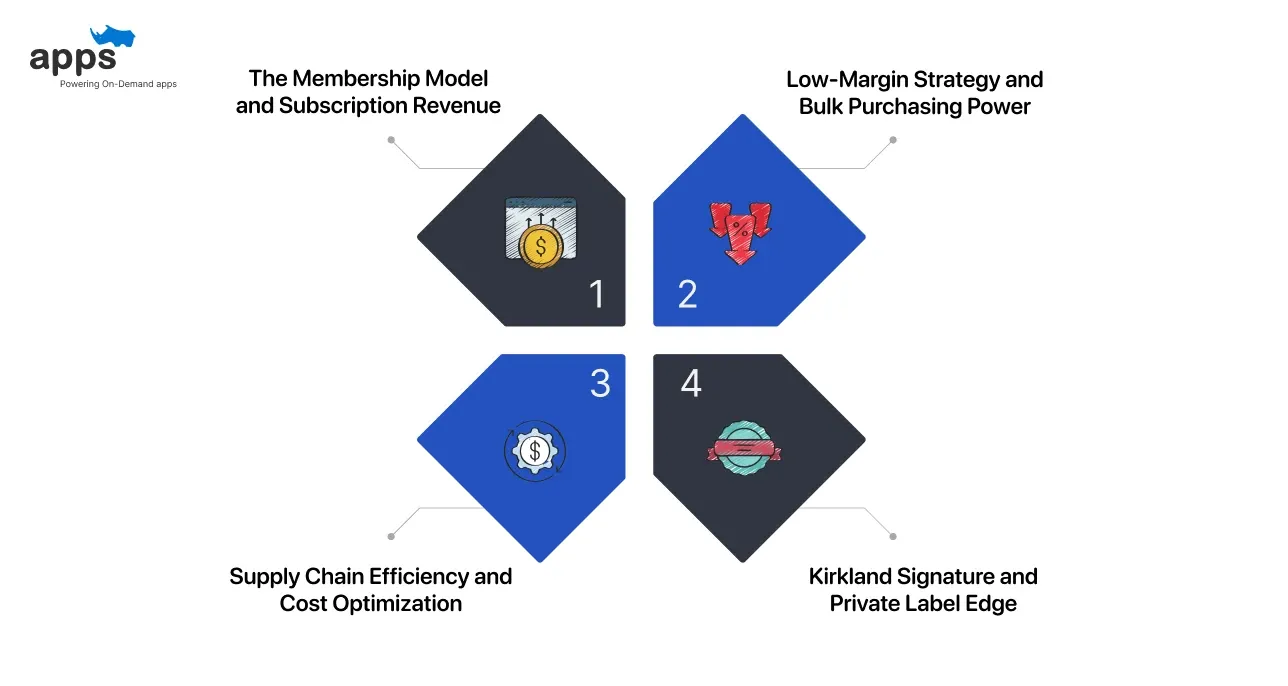
1. The Membership Model and Subscription Revenue
Costco earns differently than most retailers through its membership model.
You must pay a yearly fee to shop, and that fee becomes part of the company’s predictable subscription revenue.
- In 2024, membership fees reached about $4.8 billion, according to FinanceBuzz.
- Renewal rates typically exceed 90% indicating strong customer loyalty.
- Because many shoppers have already paid to access the store, Costco can keep product prices unusually low.
This model answers the question: how does Costco make money? Not through significant markups, but by combining subscription revenue with high-volume sales.
2. Low-Margin Strategy and Bulk Purchasing Power
Costco takes the opposite stance of high-margin retail. Its low-margin strategy focuses on selling more for less.
- Profit margins for product sales are around 11-15 %, which is low for the industry.
- The company uses bulk purchasing and stocks fewer SKUs (about 4,000) than conventional retailers do.
- Bulk items move quickly, cutting warehouse/handling costs and strengthening value.
By combining bulk buying with low markups, the wholesale strategy becomes a win for both Costco and its members: low cost for you, efficient volume for the company.
3. Kirkland Signature and Private Label Edge
One key strength of the costco business model is its private-label brand: Kirkland Signature.
- Kirkland accounts for about one-third of Costco's total sales.
- The brand uses established manufacturers behind the scenes to deliver quality at a lower cost.
- Private label lets Costco better control margins, build longer-term trust with members, and strengthen customer loyalty.
Because members associate Kirkland with value and quality, Costco doesn’t need heavy advertising. The brand becomes a powerful layer in the membership-and-value loop.
4. Supply Chain Efficiency and Cost Optimization
Costco’s operations run lean. Supply chain matters. Real amounts. The company emphasizes supply chain efficiency to support its low-cost offers and speed.
- Inventory turnover is very fast; some sources report an average of under 30 days. If you want to know how Costco achieved this, you can go through this blog and check out how they have one of the best inventory management systems.
- Warehouse design and layout follow the warehouse retailing format: large pallets, sparse décor, fewer SKUs, everything built for speed.
- By buying direct, managing fewer intermediaries, and keeping costs minimal, Costco cuts unnecessary costs and stays flexible in its pricing.
These practices make Costco’s costco pricing strategy work: consistent value, fewer surprises, and operations built to scale.
This walk-through of the central pillars of the Costco Business Model shows why it works so reliably.
Next up, we’ll map out the business structure using the Costco Business Model Canvas and visually see how all these pieces fit together.
How Does Costco Make Money – Revenue Streams and Cost Structure
Costco’s income flow is simple yet effective. The Costco business model combines recurring membership revenue, high-volume sales, and strict cost control to drive loyalty and long-term profitability.
By understanding these revenue streams and cost levers, you’ll see how Costco makes money and why it has built such a resilient business.
Membership Fees and Predictable Cash Flow
A key part of the Costco business model is its membership model, in which shoppers pay upfront for access.
- As SDC stated, in 2024, Costco pulled in about US$4.8 billion in membership fees.
- These fees represent only ~2 % of total revenue but a much larger share of profit.
- This stream ensures stability: no matter what product sales do, the fee income remains steady.
- High renewal rates (above 90 %) reinforce customer loyalty and long-term revenue, according to IIDE reports.
Because membership fees are predictable and margin-rich, Costco can sell goods at slim margins while still turning a solid profit.
Retail Sales and Product Variety
Most of Costco’s revenue comes from bulk product sales across categories such as food, electronics, apparel, and household goods.
- For example, net sales in FY2024 reached about US $249.6 billion.
- The business also serves the B2B segment through the Costco Business Center, which diversifies its customer base (i.e., small businesses) and supports the wholesale strategy.
- This product variety and scale support the warehouse retailing format, fewer SKUs but higher volume per item, with a strong emphasis on bulk purchasing.
This mix of large-scale retail sales and membership income keeps the revenue engine humming.
Ancillary Businesses and Services
Beyond bulk goods and memberships, Costco adds value and revenue through ancillary services. These include:
- Gas stations offering fuel at lower prices
- Optical centres, pharmacies, and hearing aid services
- Food courts (famous for value offerings)
- Travel and insurance services under membership perks
While each of these doesn’t drive the bulk of revenue on its own, together they enhance the customer experience, increase store visits, and boost overall spend per member.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Leadership
Costco’s competitive edge lies in its tight cost structure, and disciplined execution is a key part of its Costco pricing strategy and broader Costco business strategy.
- The company limits product mark-ups to around 11–14%, well below typical retailers'.
- AInvest research claims that it streamlines its supply chain and builds efficient warehouses, resulting in fast inventory turnover and low storage costs.
- The warehouse layout, pallet racks, minimal décor, and lean staffing drive down overhead.
- Direct sourcing helps maintain the private-label brand (e.g., Kirkland Signature) and eliminates middlemen.
All of this means Costco can offer savings to members while maintaining healthy business margins.
Costco’s revenue model and cost control form the backbone of its unique retail proposition.
In the next section, we’ll explore the Costco business model canvas and visually map how all these elements fit together into one cohesive system.
The Costco Business Model Canvas
Here’s how the pieces of the Costco business model fit together in a clear and structured way. This canvas shows how value is created, delivered, and captured across the business.
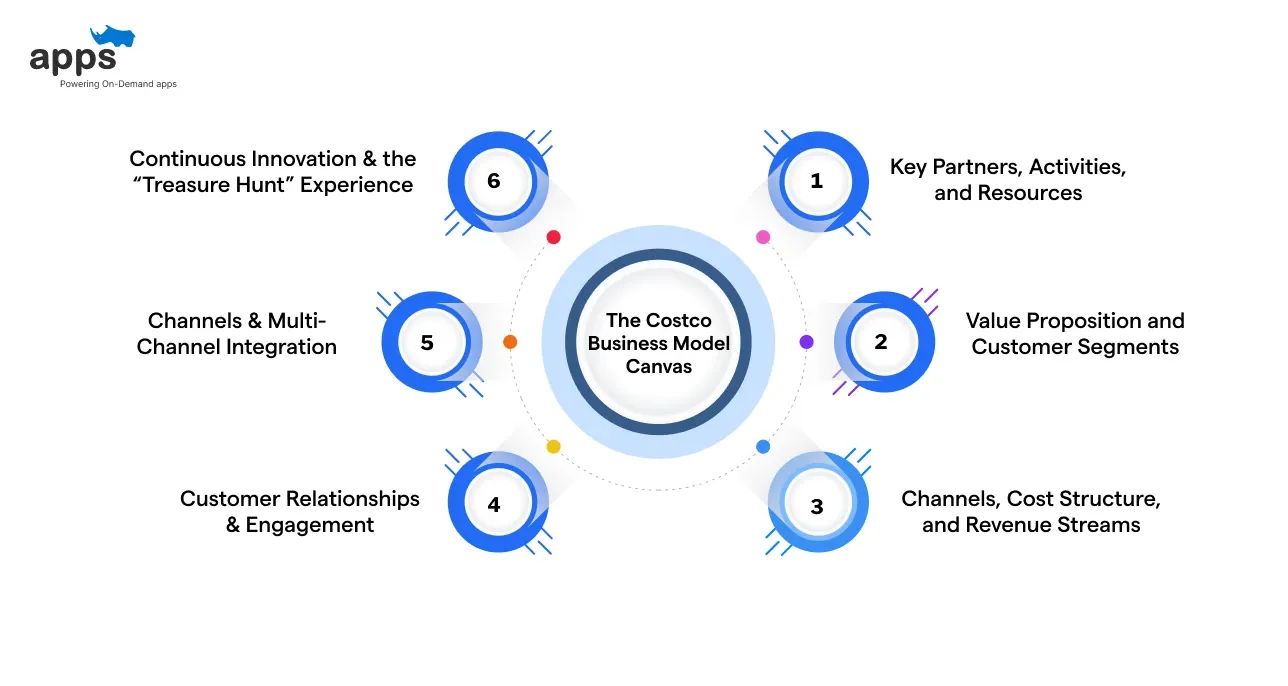
1. Key Partners, Activities, and Resources
Costco’s success begins with its strategic partnerships. The company collaborates closely with manufacturers and suppliers many behind the Kirkland Signature brand to secure exclusive products and bulk purchasing advantages.
Beyond suppliers, Costco also partners with financial institutions (like Visa for co-branded credit cards), logistics providers, and technology firms to enhance digital operations and data analytics.
Core activities include warehouse retailing, large-scale procurement, supply chain efficiency, and membership management.
Its essential resources are vast warehouse locations, advanced logistics systems, and a loyal, recurring membership base that ensures steady subscription revenue.
2. Value Proposition and Customer Segments
Costco’s value lies in its low-margin strategy offering premium goods at unbeatable prices.
Its private label, Kirkland Signature, reinforces trust through quality and affordability, giving customers more for less.
Primary customer segments include value-driven households, small businesses, and B2B clients through the Costco Business Center.
Globally, Costco tailors product variety and pricing for local markets while ensuring its wholesale strategy remains consistent across regions.
3. Channels, Cost Structure, and Revenue Streams
Channels: Physical warehouses remain Costco’s foundation, complemented by e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, and online membership services.
Cost Structure: Costco minimizes operational costs through lean inventory, limited SKUs, direct sourcing, and minimal advertising—driving superior supply chain efficiency.
Revenue Streams:
- Membership fees (subscription revenue) ensure predictable cash flow.
- Product sales from bulk purchasing drive consistent turnover.
- Private label margins (Kirkland Signature) enhance profitability.
- Ancillary income from optical, travel, fuel, and co-branded financial services contributes additional revenue.
4. Customer Relationships & Engagement
The CostCo Business Model emphasizes trust through long-term relationships. Its no-questions-asked return policy, membership renewals, and in-store experiences like product samplingenhance customer loyalty.
Costco also engages B2B buyers with tailored pricing and support through its Business Centers, aligning with its costco business strategy of inclusivity across market segments.
The company leverages costco insights resources and customer analytics to refine offerings, manage demand, and ensure consistency across regions.
5. Channels & Multi-Channel Integration
While warehouse retailing remains core, Costco is rapidly scaling its digital presence.
The brand’s integration of e-commerce, pickup & delivery, and mobile membership scanning ensures convenience for modern consumers.
Through this omnichannel strategy, Costco blends in-store experiences with online accessibility balancing tradition with technology.
6. Continuous Innovation & the “Treasure Hunt” Experience
One of the most unique aspects of costcos business model is its “treasure hunt” approach offering limited-time deals and rotating products to encourage repeat visits.
This retail psychology drives excitement, customer loyalty, and frequent footfall, differentiating Costco from rivals like the costco vs walmart business model comparison shows.
Additionally, ongoing innovation in logistics, AI-driven forecasting, and ethical sourcing strengthens the costco ethical business model and aligns with the costco wholesale in 2012 mission business model and strategy to deliver value, efficiency, and sustainability.
This updated canvas section covers both the major blocks of Costco’s model and deeper pointers (such as the treasure-hunt inventory strategy, tech partnerships, and the B2B channel).
Next, we’ll move into how Costco stacks up against its rivals in the Costco vs Walmart business model section.
Costco vs Walmart Business Model – A Strategic Comparison
Costco and Walmart both dominate global retail, but their paths to success couldn’t be more different.
Here’s a concise comparison of their core business strategies based on 2024 data from Forbes, Business Insider, and Statista.
| Feature | Costco | Walmart |
| Business Model | Membership-based warehouse retailing | Open-access retail model |
| Access Type | Paid membership required | Free access for all shoppers |
| Main Revenue Source | Membership fees & bulk product sales | Retail sales volume across broad categories |
| Pricing Strategy | Low-margin strategy with bulk purchasing | Everyday Low Pricing (EDLP) for consistent affordability |
| Average SKU Count | ~4,000 (limited, high-volume items) | 100,000+ (broad product range) |
| Private Label | Kirkland Signature – quality-focused | Great Value, Equate – price-focused |
| Customer Loyalty | Driven by ~90% membership renewals | Driven by convenience and price |
| Marketing Approach | Minimal advertising; word-of-mouth | Multi-channel marketing and online ads |
Costco wins on loyalty and trust, Walmart on scale and reach, but both redefine value in their own way.
Next, we’ll explore how Costco’s ethical practices and sustainability commitments shape its Costco Ethical Business Model.
The Ethical and Sustainable Side of Costco’s Business Model
The Costco business model emphasizes ethical sourcing, fair labour, sustainability, and transparency.
These efforts build long-term trust, strengthen customer loyalty, and ensure the brand grows responsibly.
Costco Ethical Business Model and Practices
Costco follows a strict Code of Ethics and Supplier Code of Conduct to protect human rights, labour standards, and environmental safety.
According to marketing-scoop research, employees in the U.S. earn an average of $24 per hour, with benefits for full- and part-time workers.
Panmore reports that in FY2024, Costco contributed over $84 million to community charities and relief programs.
Its supplier teams regularly audit partners to ensure safe conditions and fair practices.
Sustainability in Bulk Purchasing
Sustainability aligns naturally with Costco’s bulk purchasing model. In 2024, packaging changes in Kirkland Signature products eliminated 4 million pounds of plastic and saved nearly $8 million.
The STAR program focuses on cutting energy, water, and waste, reducing landfill impact across warehouses.
By selling in larger quantities, Costco minimizes packaging waste and shipment frequency, lowering its carbon footprint.
Long-Term Ethical Growth and Customer Trust
Costco’s mission, “For Costco to thrive, the world must thrive,” guides its ethical strategy.
The company targets a 39% reduction in Scope 1 & 2 emissions by 2030 and publishes regular ESG updates. Ethical sourcing and sustainability drive customer confidence, proving that profit and purpose can coexist.
These commitments position Costco as a trusted and responsible global retailer.
Ethical Supply Chain and Sourcing Standards
Costco enforces transparency across its global supply chain. Suppliers must disclose factory details, follow strict human rights standards, and allow third-party audits.
Products like coffee, cocoa, and seafood are ethically sourced under traceable, fair-trade programs.
This ensures Costco’s global operations remain compliant, fair, and environmentally responsible.
Renewable Energy and Carbon Footprint Reduction
Costco invests heavily in renewable operations. Solar energy powers many warehouses, and the company continues shifting to electric delivery fleets.
According to Tracenable data, in 2023, Costco reported 2.88 million tCO₂e in direct emissions, aiming for significant reductions by 2030.
These steps demonstrate measurable progress toward a cleaner, more sustainable retail network.
Ethical Leadership and Corporate Governance
Ethical leadership anchors Costco’s growth. Its governance committees oversee compliance, sustainability, and employee welfare.
Executives maintain transparent pay structures and open reporting systems.
This leadership culture ensures Costco’s expansion remains fair, honest, and people-focused.
Costco proves that responsibility and profitability can go hand in hand, making ethics a strength rather than an afterthought.
Next, we’ll explore how this model scales globally while maintaining its core values.
Costco’s Digital Transformation and E-Commerce Integration
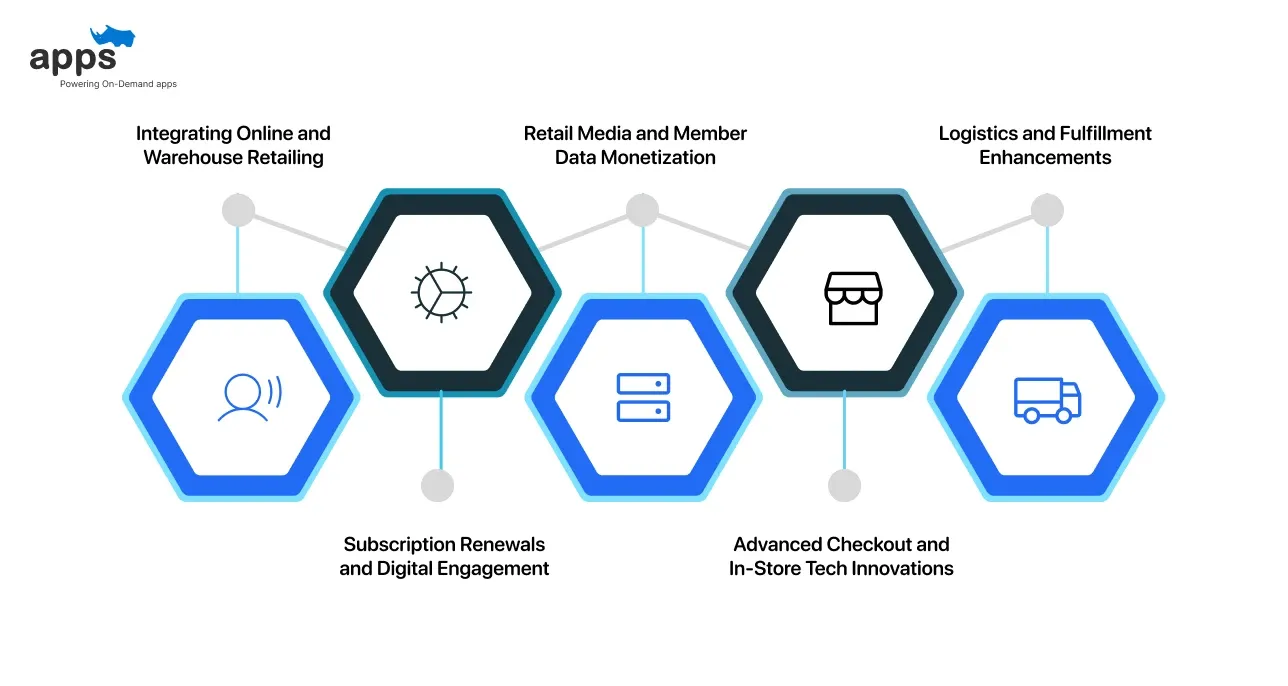
The Costco business model now merges warehouse retailing with online convenience, data-driven engagement, and modern logistics, ensuring that technology enhances, not replaces, its member-first philosophy.
Integrating Online and Warehouse Retailing
Costco’s online and physical operations work seamlessly together. Digital Commerce reports claims that Online sales grew 18.9% year-over-year in 2024, powered by expanded e-commerce listings, same-day delivery, and in-store pickup.
Members can now order bulky or out-of-stock items online and collect them from nearby warehouses. This hybrid setup helps Costco maintain its low-cost advantage while improving accessibility.
Subscription Renewals and Digital Engagement
Digital tools are reshaping Costco’s membership model and subscription revenue. Through the mobile app, users renew memberships, upgrade tiers, and access digital receipts.
Executive memberships now account for 46.5% of all members and drive over 73.5% of global sales, according to Infotechlead. This digital shift keeps engagement high and simplifies renewals, building lasting customer loyalty.
Retail Media and Member Data Monetization
Costco is quietly expanding into retail media, leveraging member insights for brand promotions and product placements. By analyzing purchase behavior, Costco offers partners targeted marketing opportunities without breaching trust.
This data-driven approach adds a new revenue stream while improving customer relevance.
Advanced Checkout and In-Store Tech Innovations
Costco is testing digital checkout experiences, such as “Scan & Pay” and self-service kiosks. These upgrades reduce wait times and enhance convenience without increasing overhead.
As Business Insider reports, in 2025, Costco began piloting mobile shopping and digital receipts in select U.S. warehouses, modernizing the warehouse retailing experience.
Logistics and Fulfillment Enhancements
Behind the scenes, Costco has optimized fulfillment for heavy and bulk items. Advanced route planning and partnerships with last-mile carriers have reduced delivery times by up to 25%.
These logistics upgrades allow Costco to scale online orders efficiently while maintaining cost discipline.
The Future of Costco’s Digital Strategy
In 2024, Costco’s e-commerce revenue hit $19.6 billion, about 7% of total sales. The next phase focuses on omnichannel expansion, personalized recommendations, predictive restocking, and warehouse-to-home delivery.
By blending technology with its wholesale roots, Costco’s digital strategy strengthens its position as a trusted, modern retailer.
Costco’s digital transformation proves innovation doesn’t have to disrupt what already works; it can enhance it.
Global Expansion and International Strategy of the Costco Business Model
The Costco Business Model has proven remarkably adaptable worldwide. Built on a strong membership model, bulk purchasing, and a low-margin strategy, Costco continues to scale across global markets while maintaining its promise of affordability and value.
Its approach combines operational efficiency, cultural awareness, and long-term customer loyalty, reinforcing why costcos business model stands as one of the most resilient in modern retail.
1. Store-Growth Pacing & Expansion Targets
Costco adds 25–30 new warehouses each year, with nearly half located outside the U.S.
According to Nasdaq reports, by 2025, the company is expected to reach 914 global warehouse locations, continuing its steady expansion strategy rooted in the Costco Wholesale mission business model.
This disciplined growth supports the subscription revenue model while sustaining brand reliability worldwide.
2. Market-Selection Strategy & Demographic Focus
The CostCo Business Model Canvas emphasizes data-driven market selection. Costco targets regions with high household income, strong car ownership, and proven interest in membership-based shopping.
SlideShare data reveals that by focusing on these demographics, Costco ensures its warehouse retailing and wholesale strategy resonates locally while driving profitability and member engagement.
3. Localization of SKU Count & Product Mix
In urban markets like China and Japan, Costco reduces its SKU count to 2,000–3,000 items while featuring more locally relevant private label and Kirkland Signature products.
This localization strengthens its customer loyalty while maintaining the efficiency of bulk purchasing and the trusted warehouse model.
4. Entering New Markets and Cultural Adaptation
From redesigned layouts to localized Kirkland Signature assortments, markets like Spain, Japan, and Canada receive tailored experiences that reflect regional preferences.
Such adaptability ensures that Costco’s business model remains relevant while delivering the same value proposition globally.
5. Global Supply Chain and Pricing Consistency
Supply chain efficiency enables Costco to maintain stable pricing and its low-margin strategy worldwide.
For example, regional sourcing in Asia-Pacific reduced costs by up to 40% on select Kirkland Signature products.
This efficiency aligns perfectly with the Costco pricing strategy, keeping prices uniform and competitive across borders.
6. Foreign Exchange and Cost Headwinds vs Benefits of Global Scale
Despite global success, Costco faces foreign-exchange risks, tariff challenges, and land costs in emerging markets.
However, its large-scale procurement, streamlined logistics, and robust wholesale strategy help offset these pressures.
This balance allows Costco to protect margins without sacrificing affordability, showcasing the strength of the costco ethical business model.
7. Challenges and Opportunities in Expansion
As Costco expands globally, the CostCo Business Model faces both hurdles and growth opportunities shaped by regional dynamics
Challenges
- High land costs and regulations in Europe and Asia slow warehouse expansion.
- Currency fluctuations and tariffs pressure the low-margin strategy.
- Local retailers with similar wholesale strategies intensify competition.
- Managing logistics globally strains supply chain efficiency.
- The membership model sees slower adoption in non-subscription markets.
Opportunities
- Expansion in Latin America and Asia drives bulk purchasing growth.
- Digital integration boosts customer loyalty and subscription revenue.
- The costco ethical business model strengthens brand credibility.
- Localized Kirkland Signature and private label lines boost appeal.
- A strong global reputation reinforces the Costco business model.
Through these challenges and opportunities, the CostCo Business Model continues to evolve, balancing global efficiency with local relevance.
It merges global reach with local relevance showing exactly how does costco make money while sustaining its promise of value, quality, and trust.
Key Lessons Businesses Can Learn from the Costco Business Model
The Costco Business Model is a blueprint for sustainable growth built on value, trust, and efficiency. Here are seven key lessons modern businesses can apply to build loyal customers and long-term profitability.
1. Build a Membership Ecosystem
Recurring income from a membership model ensures stability and strengthens customer loyalty through exclusivity and engagement.
2. Prioritize Value Over Margin
Adopting a low-margin strategy builds trust, offering consistent quality at fair prices, drives repeat purchases, and word-of-mouth growth.
3. Streamline Supply Chains
Direct sourcing and supply chain efficiency reduce costs and improve delivery speed, creating a lasting advantage in wholesale strategy.
4. Focus on Scale, Not Variety
Fewer SKUs and bulk purchasing allow operational simplicity and pricing control, key pillars of the Costco business model canvas.
5. Invest in Ethical Operations
The costco ethical business model proves that responsible sourcing and fair labor practices enhance reputation and loyalty.
6. Use Private Label Power
Brands like Kirkland Signature show that private label products can build trust and deliver high margins while keeping prices low.
7. Embrace Digital Integration
Combining warehouse retail with online sales and subscription revenue strengthens omnichannel engagement and customer retention.
Each of these principles makes the Costco Business Model a masterclass in balancing efficiency, value, and sustainability.
Conclusion
The brilliance of the Costco Business Model lies in its simplicity: deliver value, earn trust, and scale through efficiency. Costco didn’t just master retail; it reinvented it through its membership model, low-margin strategy, and relentless focus on customer loyalty.
Every decision from bulk purchasing to supply chain efficiency reflects a system built for long-term success, not short-term wins.
That same principle drives growth in the digital age. Businesses that optimize operations and create seamless ecosystems thrive, just as Costco does.
At AppsRhino, we bring that same discipline to digital transformation. Whether you’re building a warehouse management system, on-demand platform, or custom retail solution, we design apps that streamline operations and maximize ROI.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does Costco actually make money?
Costco makes money mainly through membership fees, bulk product sales, and private-label brands like Kirkland, keeping prices low while earning steady profits from loyal members.
What kind of business is Costco?
Costco is a membership-based wholesale retail business that sells products in bulk at discounted prices, catering to both individuals and small businesses seeking cost savings.
What makes Costco so successful?
Costco’s success comes from its low-price strategy, limited product selection, strong supplier relationships, and loyal membership base, creating consistent sales volume and customer trust.
What makes Costco different from other stores?
Costco differs through its membership model, bulk pricing, limited markup, and emphasis on value and quality, offering premium products at lower costs than traditional retailers.
What makes Costco’s membership model different from other retailers
The membership model builds loyalty by offering exclusive access, better pricing, and rewards. It also generates steady subscription revenue that supports Costco’s long-term wholesale strategy.
How does Kirkland Signature contribute to Costco’s success?
Kirkland Signature and Costco’s private label ensure quality control and better profit margins, helping maintain customer loyalty while reinforcing the brand’s reputation for value and trust.
Can small businesses adopt elements of the Costco Business Model?
Yes, small businesses can apply principles such as bulk purchasing, transparent pricing, and customer-focused loyalty programs to replicate Costco’s scalable, efficient business strategy.
Table of Contents
- What is Costco?
- Understanding the Costco Business Model
- How Does Costco Make Money – Revenue Streams and Cost Structure
- The Costco Business Model Canvas
- Costco vs Walmart Business Model – A Strategic Comparison
- The Ethical and Sustainable Side of Costco’s Business Model
- Costco’s Digital Transformation and E-Commerce Integration
- Key Lessons Businesses Can Learn from the Costco Business Model
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)