- Origins of Zomato – An Overview
- Zomato Business Model – How Zomato Works
- Core Components of the Zomato Business Model
- Customer Segments in the Zomato Business Model
- Zomato Value Proposition – Why Users Choose Zomato
- Zomato Revenue Model – How Zomato Earns Money
- Zomato vs Swiggy – Quick Comparison
- Challenges Faced by Zomato
- Future of Zomato – Growth, Expansion, and Strategy
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Table of Contents
Zomato Business Model: How It Powers Food Delivery Success

Most people use Zomato without ever stopping to ask a simple question: How does this app actually make money by delivering a 200-rupee meal? The truth is, the Zomato Business Model is far more complex and far more profitable than just food delivery.
What started as a basic restaurant-menu site has evolved into one of India’s most powerful food delivery apps, combining logistics, advertising, subscriptions, and restaurant technology into a single ecosystem.
Whether someone is searching what is Zomato, comparing Zomato vs Swiggy, or simply tracking their next order, they’re interacting with a platform built on smart business model design and disruptive strategy.
This blog breaks down how the business model of Zomato actually works, how Zomato earns money from multiple sources, and why it remains a market leader in Zomato India’s fast-growing food-tech space.
Origins of Zomato – An Overview
Zomato’s story started as a simple fix to a common problem: finding restaurant menus easily. What began as a small idea eventually transformed into one of India’s most influential food delivery apps, shaping how millions discover and order food.
If you are asking what Zomato is and how it works, understanding this journey helps explain how the Zomato Business Model became a global success.
Understanding this journey helps explain how the Zomato Business Model became a global success.
How Zomato Started (From FoodieBay to a Global Brand)
In 2008, Deepinder Goyal and Pankaj Chaddah noticed colleagues struggling to access restaurant menus during lunch breaks. They uploaded scanned menus online, calling the platform FoodieBay.
As the website grew quickly, they rebranded to Zomato in 2010 to build a unique, global identity. The platform soon expanded into reviews, ratings, reservations, and later food zomato delivery, paving the way for Zomato’s modern business model.
Key Milestones
Zomato’s evolution accelerated through major strategic moves:
- Zomato app launch: Made discovery and ordering fast and straightforward.
- Zomato Gold, Pro, and Pro Plus: Built recurring revenue with subscription perks.
- Delivery ecosystem: A strong network of delivery partners improved speed and reliability.
- Acquisitions: Uber Eats India, Blinkit, and restaurant-tech startups strengthened operations.
- Global expansion: Zomato entered 20+ markets, boosting its brand presence.
These milestones shaped how Zomato earns money and positioned the brand as a leader in food-tech.
Zomato Business Model – How Zomato Works
Zomato runs on a simple idea connect hungry users to nearby restaurants and deliver food fast. Its operating model links customers, restaurants, and delivery partners in a smooth, coordinated flow.
Here’s how the Zomato Business Model works step-by-step.
User Journey
- Search & Discover: Users open the Zomato app to explore restaurants, cuisines, ratings, prices, and offers.
- Place Order: They add items to the cart, apply any promo code if available and pay online or opt for COD.
- Live Tracking: Zomato updates each stage, order accepted, food prepared, picked up, and on the way.
- Review & Feedback: After delivery, users rate the food, share photos, and write reviews that help future customers.
Restaurant Partner Workflow
- Order Management: Restaurants receive orders instantly and accept them with one tap.
- Menu & Pricing Controls: They manage menus, pricing, stock, offers, and discount coupons.
- Visibility & Growth: Restaurants use ads, promotions, and insights to increase visibility and reach more customers.
- Order Handover: Once the food is ready, it’s packed and handed to the Zomato-assigned delivery partner.
Delivery Partner Workflow
- Smart Assignment: Zomato’s algorithm assigns orders based on distance, availability, and delivery efficiency.
- Pickup & Delivery: Partners collect the order, navigate optimized routes, and deliver it.
- Earnings Model: Delivery partners earn through base pay, distance pay, surge pricing, and incentives.
Zomato’s smooth coordination across all three sides is what makes the platform fast, reliable, and scalable, setting the stage for how it earns money next.
Core Components of the Zomato Business Model
Zomato runs on a multi-layered system that connects customers, restaurants, and delivery partners while using technology to keep everything fast and efficient.
These core components explain how the Zomato Business Model scales across India and beyond. Here’s a simple breakdown of the pillars that power Zomato every day.
1. Marketplace Aggregator Model
Zomato works as a two-sided marketplace where users discover restaurants, compare menus, explore reviews, and place orders. Restaurants gain visibility, customer reach, and tools to manage demand through the Zomato business app.
2. Hyperlocal Delivery Network
Zomato uses a hyperlocal logistics system to deliver food quickly.
Its routing algorithms assign the closest delivery partner, optimize travel time, and ensure real-time tracking for users and restaurants.
3. Technology-Driven Platform
The Zomato app uses machine learning for personalized recommendations, intelligent search, and dynamic wait times. Its tech stack supports mapping, payments, live order tracking, and a smooth user experience across devices.
4. Subscription Model (Gold, Pro, Pro Plus)
Zomato’s subscription programs offer users benefits like priority delivery, free delivery, and exclusive dining discounts. These models boost loyalty, repeat orders, and predictable revenue while improving customer acquisition for restaurants.
5. Supply Chain Backbone
Hyperpure provides partner restaurants with high-quality ingredients, packaging, and kitchen supplies. This improves food quality, standardization, and profitability, and strengthens the entire Zomato ecosystem.
6. Quick Commerce Through Blinkit
Zomato’s integration with Blinkit adds instant grocery delivery to its portfolio.
This expands revenue streams, increases order frequency, and strengthens Zomato’s position in the delivery apps landscape.
To understand this primary growth driver, read about the business and Blinkit’s revenue model.
Together, these pillars shape a powerful, scalable, and modern business model of Zomato, one built for speed, convenience, and growth.
Customer Segments in the Zomato Business Model
Zomato serves multiple audiences simultaneously, and this multi-sided approach is what strengthens Zomato business model. Each segment interacts with the platform differently, creating value for the entire ecosystem.
Here’s a clear, concise breakdown of who Zomato caters to and why each group matters.
Customers (Delivery + Dining Out Users)
Customers use the Zomato app for convenience, quick ordering, table bookings, reviews, and real-time tracking. Food coupons, discount coupons, personalized offers, and fast food Zomato delivery drive them.
Restaurants (Small, Mid, Enterprise Chains)
Restaurants rely on Zomato for visibility, digital menus, customer acquisition, and order volume.
They also use Zomato’s delivery logistics, analytics, and Hyperpure supply chain for better operations.
Delivery Partners (Gig Workforce)
Delivery partners form Zomato’s hyperlocal backbone. They earn through flexible shifts, surge payouts, incentives, and partner benefits while enabling fast delivery turnarounds.
Advertisers and Brand Partners
Brands use Zomato for high-intent visibility through sponsored listings, banner ads, and in-app promotions. This boosts reach, conversions, and targeted customer engagement.
Dine-Out & Experience Users
Zomato caters not only to delivery users but also to diners, offering table-booking features and in-restaurant payments. This segment drives restaurant foot traffic and loyalty, and helps expand the reach of the Zomato business app beyond delivery.
These segments work together to power a seamless and scalable business model of Zomato, ensuring growth for every stakeholder in the ecosystem.
Zomato Value Proposition – Why Users Choose Zomato
Zomato’s success depends on a clear and strong value proposition that serves every group in its ecosystem. Whether it’s customers looking for convenience, restaurants seeking growth, or advertisers targeting the right audience, Zomato delivers benefits that keep each segment engaged.
These value pillars also strengthen the overall Zomato Business Model, making it competitive and scalable.
For Customers
Zomato creates a seamless experience for millions of users across India and global markets.
- Anytime convenience: Quick access to food delivery, dining-out options, and table reservations.
- Wide variety: Thousands of restaurants, cuisines, and curated food discovery experiences.
- Fast delivery: Hyperlocal logistics ensure quick, reliable food delivery.
- Personalized suggestions: AI-powered recommendations based on tastes, trends, and past orders.
- Smart savings: Deals, food coupons, discount coupons, and promo offers like the Zomato promo code.
For Restaurants
Zomato acts as a powerful growth engine for restaurants of all sizes.
- High visibility: Reach a massive audience through the Zomato app and top search rankings.
- Customer insights: Data analytics help restaurants optimize menus, pricing, and demand patterns.
- Operational support: Delivery logistics reduce the need for in-house fleets.
- Supply chain via Hyperpure: Access to high-quality ingredients and standardized supplies.
For Delivery Partners
Zomato provides a flexible livelihood opportunity for its gig workforce.
- Work flexibility: Partners choose when and how much they want to work.
- Transparent earnings: Clear payouts, incentives, and surge bonuses during peak hours.
- Digital-first workflows: Easy navigation, order updates, and support through the delivery app.
For Brands and Advertisers
Zomato serves as a high-performing advertising channel for businesses.
- Targeted visibility: Brands promote themselves through sponsored listings and banner placements.
- Precise audience targeting: Ads based on cuisine preferences, location, and customer behavior.
- High-intent users: Advertisers reach customers who are already in a “purchase-ready” mindset.
For Investors and the Business Ecosystem
Zomato also delivers substantial value to investors and the broader business ecosystem through a balanced, multi-vertical strategy.
- Diversified growth engines: Revenue from delivery, dining, ads, Hyperpure, and Blinkit reduces dependence on a single stream.
- Strong platform network effects: Millions of users, restaurants, and delivery partners reinforce long-term demand and brand stickiness.
- Improving profitability & unit economics: AI-driven routing, automation, and scale steadily improve margins and operational efficiency.
- Future-ready expansion strategy: Strategic moves like Hyperpure and Blinkit strengthen Zomato’s position in India’s digital commerce landscape.
Zomato’s value extends deep into its ecosystem, offering stability and long-term potential.
Now we have the most important and interesting section to uncover: how Zomato earns money.
Let’s find out how.
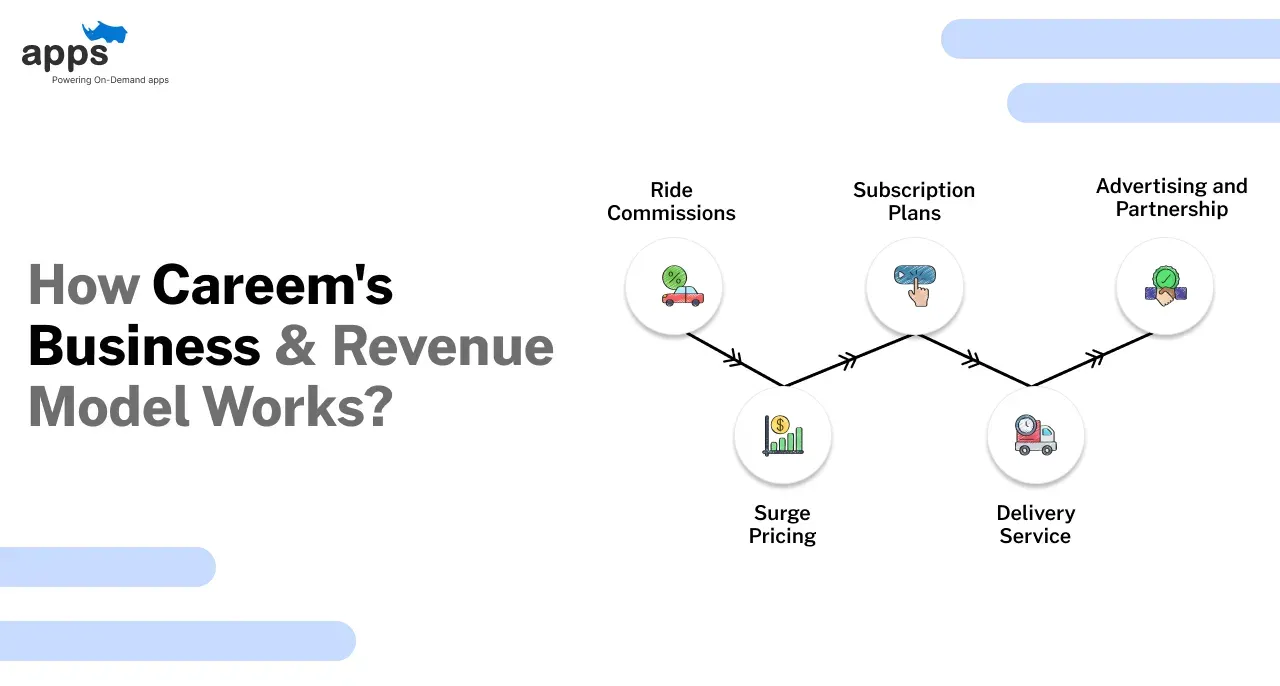
Zomato Revenue Model – How Zomato Earns Money
Zomato has moved from being “just a food delivery app” to a multi-revenue platform. Food delivery, quick commerce, B2B supplies, and subscriptions now all contribute to its growth.
According to reports shared by Zomato, in FY24, Zomato (now Eternal Ltd) reported consolidated adjusted revenue growth of about 61 percent year on year, followed by a further 70 percent jump in adjusted revenue in Q1 FY26 to ₹7,167 crore, driven heavily by Blinkit and Hyperpure.
Here’s how the Zomato Business Model actually makes money today.
Delivery Commissions
A large share of Zomato’s revenue still comes from commissions charged to restaurants on each food Zomato delivery order.
- Zomato typically charges restaurants a commission on the order value; industry commentary suggests this is often in the low- to mid-20 percent range, with newer rivals like Rapido positioning themselves at “nearly half” of Zomato and Swiggy’s commission to lure partners.
- Geojit reports show that, in Q4 FY24, Zomato’s India food ordering and delivery segment revenue grew 48.4 percent year on year to ₹1,739 crore, reflecting both higher order frequency and a larger transacting user base of about 19 million.
These commissions remain the backbone of Zomato's business model, even as other verticals scale.
Delivery Charges and Customer Fees
Alongside commissions, Zomato also earns from customer-side fees on each order.
- Zomato charges a platform fee on most orders; ahead of the 2025 festive season, this was increased from ₹10 to ₹12 per order (excluding GST), according to The Times of India reports, mirroring a similar move by Swiggy.
- Users also pay delivery charges, which vary based on distance, time, and demand, as well as packaging charges and taxes. Together, these fees help cover last-mile delivery logistics and improve unit economics.
This mix of small per-order fees, at scale, adds a meaningful layer to Zomato’s revenue model.
Subscription Revenue – Gold, Pro, Pro Plus
Zomato has experimented with several subscription programs (Gold, Pro, Pro Plus) to improve retention and order frequency.
- These plans typically offer discount coupons, free delivery, and dining benefits in exchange for a recurring fee.
- Management has indicated in shareholder letters that subscription revenue is bundled within the broader food delivery segment and helps drive higher ordering frequency and customer loyalty, which, in turn, indirectly boosts commission and fee revenue.
For users, these programs act like a “food membership”; for Zomato, they are a stickier, higher-margin layer on top of core orders.
Restaurant Advertising and Sponsored Listings
Beyond transactions, Zomato monetizes attention inside the Zomato app.
- Restaurants can pay for sponsored listings, banner ads, and priority placement in search results, especially during peak times or festivals.
- This advertising revenue scales with customer acquisition and daily active users. More eyeballs on the app means more value for restaurants paying for visibility.
Advertising gives Zomato a margin-rich revenue stream that is less dependent on individual order economics.
Hyperpure B2B Revenue Stream
Hyperpure is Zomato’s B2B supply chain business, supplying fresh ingredients and kitchen essentials to restaurants and, now, to non-restaurant partners as well.
- In Q3 FY24, Hyperpure revenue more than doubled year on year to ₹859 crore, and then climbed to ₹951 crore in Q4 FY24, a 99 percent YoY increase, driven by a larger B2B opportunity and more value-added products.
- By Q4 FY25, Hyperpure’s revenue from non-restaurant businesses, primarily Blinkit sellers, reached ₹1,840 crore, accounting for around 62 percent of Hyperpure's revenue.
Hyperpure earns through supply-chain margins by buying at scale and selling standardized, high-quality inputs, and has become a key pillar of the modern Zomato Business Model.
Blinkit Contribution – Quick Commerce Revenue
Blinkit is now the fastest-growing part of the group and a significant reason investors watch Zomato vs Swiggy and Zepto so closely.
- Economic Times reports that for FY24, Blinkit’s revenue from operations almost tripled to ₹2,301 crore, up from ₹806 crore the previous year.
- In Q4 FY24, Blinkit revenue touched ₹769 crore, up 111.8 percent year on year, and turned adjusted EBITDA positive in March 2024, meaning the quick commerce unit was finally contribution-profitable at an operating level.
- By Q1 FY26 (quarter ending June 30, 2025), Eternal (Zomato’s parent) reported that Blinkit’s net order value surpassed the core food delivery business for the first time, with consolidated adjusted revenue up 70 percent year on year to ₹7,167 crore, primarily driven by quick commerce growth, according to reports.
Today, Blinkit is not just a side business; it is reshaping how Zomato earns money and where future growth comes from.
Events, Catering, and Corporate Services
Zomato also generates smaller but strategic revenue from dining out, events, and corporate solutions.
- This includes table reservations, Zomato-branded events, and enterprise catering partnerships, often bundled with marketing and platform visibility.
- While these streams are not broken out in detail, they support the overall business model design by strengthening relationships with high-value restaurants and corporate clients.
These lines diversify the Zomato revenue model beyond pure delivery and help position Zomato as a broader food and experiences platform.
Zomato’s revenue model is layered, with evolving food delivery remaining core, but supply chain, quick commerce, subscription, and ads all playing increasing roles.
In the next section, you can unpack how this model stacks up in a Zomato vs Swiggy comparison and what it means if you are planning to build your own food delivery product.
Zomato vs Swiggy – Quick Comparison
Here’s a quick comparison of how the two big players in India’s food delivery world differ in key metrics, features, and strategies.
It helps clarify how the Zomato Business Model compares with its main competitors.
Metric | Zomato (Eternal Ltd) | Swiggy Ltd | Key Differentiators |
| Unique Features | Hyperpure (B2B supplies), InterCity Legends, Blinkit + food delivery combo | “Drops” limited-edition menu items, strong logistics tech | Zomato's deeper ecosyste.; Swiggy's stronger logistics innovation |
| FY 25 Revenue | ₹20,243 crore (+67 % YoY) (Estimated) | ₹15,227 crore (+35 % YoY) (Estimated) | Zomato leads in size and growth rate |
| Quick-Commerce Share & Growth | Blinkit AOV ~₹660, GOV up >120% | Instamart AOV ~₹499, GOV growth ~118% | Zomato is ahead in the ultra-fast segment by AOV and growth |
| Subscription/Membership | Zomato Pro/Plus is heavy on “dine-in + delivery” perks | Swiggy One focuses on frequent small-order free delivery | Zomato leans premium; Swiggy leans towards value. |
| Coverage & App Features | 800 cities in India; strong in big metros | 580+ cities; strong tier-2/3 city penetration | Swiggy is more widespread; Zomato is deeper in metros. |
Zomato currently leads in revenue, profitability, user base, and quick commerce growth, while Swiggy remains strong in regions, service dept, and brand engagement.
Understanding these differences helps you decide which model aligns better if you're building your own on-demand app or planning to partner.
Challenges Faced by Zomato
Even with a strong Zomato Business Model and growing revenue, the business runs on thin ice. Profitability, quick commerce, and workforce expectations make this a challenging market to operate in, not just to lead.
Here are the key challenges Zomato India is navigating right now.
High Operating Costs and Thin Margins
Food delivery is a low-margin game. Reports show that in Q4 FY25, Zomato’s operating margin was around 1.2 percent, pulled down by higher costs from rapid Blinkit store expansion and operating expenses.
Even though Eternal (Zomato) reported operating revenue of about ₹20,243 crore and roughly ₹527 crore in profit in FY25, management commentary repeatedly flags pressure from store ramp-ups and subdued demand, especially in food delivery.
Quick commerce is growing fast, but still drags margins. Blinkit has seen strong order growth, yet continues to post core losses as Zomato invests in new dark stores, technology, and delivery capacity.
Heavy Discounts and Customer Acquisition Cost
India’s food delivery market is addicted to deals. A 2025 industry report by GlobeNewswire
notes that platforms like Zomato India and Swiggy rely on deep discounts and aggressive promotions, which push customer acquisition cost and operational spend up, hurting profitability.
To retain high-frequency users, Zomato runs promo campaigns and offers food and discount coupons, while also pushing subscription products like Pro and Pro Plus.
That builds loyalty but makes it harder to improve unit economics steadily.
Newer entrants and even mobility players like Rapido, entering food delivery with lower commission models, add more price pressure, forcing incumbents to balance commissions, discounts, and sustainable margins, according to The Financial Express.
Competitive Pressure From Swiggy and Other Players
Reports from Indomoney show that the Zomato vs Swiggy battle is still intense. As of FY25, Zomato leads in revenue and active ordering users, but Swiggy continues to compete vigorously, especially in specific regions and service categories.
In quick commerce, Blinkit faces fierce competition from Swiggy Instamart, Zepto, BigBasket and Flipkart.
Reuters reports show that Blinkit holds about 46 percent market share but still faces strong price and service pressure as rivals invest heavily.
On top of that, India’s ONDC initiative and new regional apps broaden the competitive landscape, pushing Zomato to continue innovating its business model, delivery logistics, and customer acquisition playbook.
Regulatory and Workforce Challenges
Zomato’s delivery fleet is part of India’s growing gig economy. NITI Aayog estimated around 7.7 million gig workers in 2020, projected to reach 23.5 million by 2030, with Zomato, Swiggy, Ola, and Uber as major platforms.
Reports like Fairwork India 2024 highlight concerns around pay transparency, social security, and working conditions for gig workers on platforms such as Zomato and Swiggy.
This raises regulatory risk and reputational pressure, pushing platforms to revisit incentives and policies.
Any new labour code or platform-specific regulation could impact the Zomato Business Model, especially around per-order payouts, insurance, and social protection for delivery partners.
Demand Volatility and Macro Slowdowns
Even with strong top-line growth, Zomato is exposed to shifts in consumer spending. Reuters reported that in one recent quarter, net profit fell by more than 50 percent year on year, despite 64 percent revenue growth, because of higher costs and a demand slowdown after the festive season.
Food delivery and quick commerce are discretionary.
Any macro dip, inflation spike, or change in customer habits can quickly hit order volumes and average order values, putting extra stress on already thin margins.
Taken together, these challenges show that even a large, successful food delivery app like Zomato must keep refining its costs, logistics, and workforce strategy to stay ahead.
Next, it is crucial to examine where the Zomato Business Model is headed and what the future of food delivery could look like.
Future of Zomato – Growth, Expansion, and Strategy
Zomato’s path forward is no longer just about food delivery. The company is actively shifting toward quick commerce, B2B supply, and tech-driven operations to scale sustainably.
These moves are central to understanding how the Zomato Business Model will evolve over the next decade.
Scaling Blinkit and Quick Commerce
- In January 2025, Zomato injected ₹500 crore into Blinkit, bringing its total investment to approximately ₹2,800 crore since the acquisition in August 2022.
- Blinkit has opened over 1,200 dark stores by early 2025 and targets 2,000 micro-warehouses by 2026 to enable ultra-fast deliveries across India, according to Business Model Canvas reports.
- In Q1 FY26, Zomato’s parent saw Blinkit’s order value surpass the core food delivery business for the first time, marking a significant shift in its growth lever.
Expanding Hyperpure Nationwide
- The B2B supply chain arm Hyperpure has been doubling annual revenue in recent years and is expanding from restaurants into non-restaurant retail channels.
- Zomato plans to integrate the supply-chain vertical more deeply with Blinkit and restaurant operations, leveraging economies of scale and standardised inventory.
AI, Automation, and Route Optimization
- Zomato is deploying advanced AI across logistics: route planning, demand forecasting, and real-time delivery optimisation.
- In April 2025, Zomato laid off around 600 employees and said automation and tech upgrades were key to improving margins.
- The rebranding to Eternal Ltd. in February 2025 signals a broader tech-first vision beyond food delivery.
Long-Term Profitability Path
- With the business stretching into quick commerce, supply chain, and events, Zomato is working to diversify away from slim-margin food delivery alone.
- Future growth will depend on achieving scale in Blinkit and Hyperpure while improving unit economics via automation and fewer discounts.
- Analysts suggest that if Blinkit continues its momentum, it could become Zomato’s dominant vertical within 1–2 quarters.
Zomato’s next chapter focuses on expanding its ecosystem, not just selling meals. By scaling quick commerce, the supply chain, and tech infrastructure, the company is reshaping Zomato's business model for long-term depth and resilience.
Conclusion
The Zomato Business Model proves one thing: great platforms win when they blend smart tech, fast delivery, and a seamless customer experience. And as we saw, Zomato didn’t grow by chance. It scaled through strong logistics, a tight marketplace engine, and continuous product innovation.
If you're exploring this model, you’re likely thinking about building something simila,r maybe a food delivery app, a hyperlocal platform, a marketplace, or even a quick-commerce solution.
For inspiration on your next venture, you can explore the latest On-Demand Mobile App Ideas and Trends.
That’s precisely where AppsRhino becomes valuable. We help businesses build Zomato-like apps with the same speed, reliability, and intelligence, minus the complexity, cost, and years of experimentation.
You bring the idea.
We bring the execution.
Why AppsRhino Is the Ideal Partner?
- 8+ Years of Experience: Delivered 200+ projects, worked in 22+ countries and in 35+ industries.
- Full White-Labeling: Launch under your brand with complete customization.
- Food Delivery Expertise: Complete Zomato-like ordering, menus, ratings, and tracking.
- Real-Time Logistics: Smart routing, batching, and driver assignment algorithms.
- Marketplace-Ready System: Multi-vendor setup for food, grocery, pharmacy, or services.
- Quick Commerce Capability: Blinkit-style 10–20 min delivery infrastructure.
- Restaurant & Vendor Tools: POS integrations, menus, pricing, offers, and analytics.
- AI-Powered Features: Recommendations, demand forecasting, and dynamic notifications.
- High-Scale Architecture: Built to support multi-city traffic and peak demand.
- End-to-End Support: UI/UX, development, integrations, QA, DevOps, and maintenance.
AppsRhino turns ambitious ideas into high-performance platforms built for real growth. If you want the speed of an on-demand launch and the power of enterprise tech, your next step starts here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Zomato profitable today?
Yes, Zomato turned profitable in FY24 and continues improving margins through the Zomato Business Model, driven by Blinkit, Hyperpure, and higher-order frequency across Zomato India.
How much commission does Zomato take from restaurants?
Zomato charges restaurants a commission typically ranging between 15% to 30%, depending on location, demand, order volume, and promotional visibility inside the Zomato app.
What is the business model of Zomato?
The Zomato Business Model works on a marketplace aggregator system, connecting users, restaurants, and delivery partners. It earns through commissions, ads, delivery fees, subscriptions, Hyperpure, and Blinkit’s quick-commerce revenue streams.
Does Zomato use AI in its food delivery operations?
Yes. Zomato uses AI for route optimization, demand prediction, personalized recommendations, and improving delivery logistics across its marketplace, helping reduce wait times and operational costs.
Can small restaurants benefit from the Zomato Business Model?
Absolutely. Zomato gives small restaurants visibility, customer acquisition, access to food delivery apps, rating systems, analytics, and supply-chain support through Hyperpure to scale faster.
How does Zomato compare to Swiggy in terms of expansion and strategy?
Both compete closely, but Zomato’s growth is strengthened by Blinkit, Hyperpure, and aggressive business model design. Many users still compare Zomato vs Swiggy for pricing, speed, and offers.
Does Zomato use different strategies for Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 cities?
Yes. Zomato adjusts pricing, delivery fleets, discount coupons, and partner onboarding based on city demand to maintain efficiency and reduce operating costs.
How does Zomato ensure food quality through Hyperpure?
Hyperpure supplies fresh ingredients and standardized materials directly to restaurants, ensuring better hygiene, consistent taste, and improved customer experience across partner outlets.
Table of Contents
- Origins of Zomato – An Overview
- Zomato Business Model – How Zomato Works
- Core Components of the Zomato Business Model
- Customer Segments in the Zomato Business Model
- Zomato Value Proposition – Why Users Choose Zomato
- Zomato Revenue Model – How Zomato Earns Money
- Zomato vs Swiggy – Quick Comparison
- Challenges Faced by Zomato
- Future of Zomato – Growth, Expansion, and Strategy
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions