- Introduction
- The Benefits of Telemedicine
- Telemedicine Applications in Different Fields
- Challenges and Solutions
- Future Trends in Telemedicine
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Table of Contents
What Makes Telemedicine Applications the Future of Healthcare

Introduction
Imagine receiving quality healthcare services, getting your medications delivered, and conducting regular meetings with the healthcare provider of your choice. Sounds both comfortable and convenient, right? This comfort and convenience have been brought to life by introducing telemedicine applications in healthcare.
There’s no doubt that the wonders of the digital world catch our individual lives. This has increased to the extent that we look for a virtual alternative for every domain in the market. In addition, healthcare organizations have stepped up their game and established telemedicine applications in their existing systems.
Telemedicine applications are a revolution in the world of healthcare. These applications enhance patient satisfaction by offering personalized and exclusive healthcare services. The services offered by telemedicine applications can be used by patients at their convenience, making them extremely accessible.

Additionally, integrating these applications has given rise to streamlined workflows within healthcare organizations. Therefore, it is an ideal choice for both healthcare providers and patients alike.
This blog post further delves into the benefits and advantages of switching from conventional ways to telemedicine applications and how healthcare organizations can utilize them for their own good.
The Benefits of Telemedicine
The extensive benefits offered by healthcare organizations are as follows:
Convenience and Accessibility
The primary reason why telemedicine applications are the go-to choice for both healthcare providers and patients is because of the convenience and accessibility it offers. Patients can receive medical aid at any time of the day.
These applications have made exclusive healthcare services accessible to people who reside in rural or low-lying areas. All they need to do is install this application on their mobile phones and update their credentials, and they are good to go.
Cost-Effectiveness
Creating telemedicine applications right from scratch might seem like a costly affair, but it's not. For this, healthcare organizations can partner up with institutions that have end-to-end solutions when it comes to developing applications right from the beginning.
One such institution is AppsRhino. It has a proven record of developing the most popular healthcare applications in the market. AppsRhino also offers various pricing models for developing applications. Healthcare organizations can look into them and choose the one that best suits their needs.
Improved Patient Experience
There has been a significant increase in patient experience right after the inclusion of telemedicine applications. This is mainly because of the numerous features it has in store for its users.
Features like virtual consultations allow patients to consult their medical professionals from anywhere they wish to. The scheduled appointments are flexible to the patient’s plan, making it even more convenient for them. The presence of a communication platform further fosters trust and transparency between the two parties.
Telemedicine Applications in Different Fields
Telemedicine applications have further branched into different categories. The following section discusses the different fields where these applications can be put to use.
Teleconsultation
Teleconsultation is at the forefront of telemedicine applications. It enables patients to interact with healthcare providers through video consultations. This allows for remote diagnosis and treatment options, reducing the need for physical visits.
Moreover, teleconsultation also facilitates the monitoring of patients through telehealth devices, enabling healthcare professionals to track vital signs and other relevant health data remotely.
Telepsychiatry

Telepsychiatry employs telemedicine to provide remote mental health services. It allows for psychiatric evaluations, therapy sessions, and medication management through virtual consultations.
Telepsychiatry is particularly beneficial for individuals living in areas with limited access to mental healthcare services. It helps overcome barriers such as stigma and transportation issues, making mental health support more accessible and convenient.
Telecardiology

Telecardiology utilizes telemedicine to remotely monitor and manage heart conditions. Through the use of specific devices, such as wearable heart monitors and remote ECG machines, healthcare professionals can gather real-time data and interpret it for diagnosis and treatment.
Telecardiology plays a crucial role in early detection and prevention of cardiac emergencies, providing timely interventions and reducing the risks associated with heart-related conditions.
Teledermatology
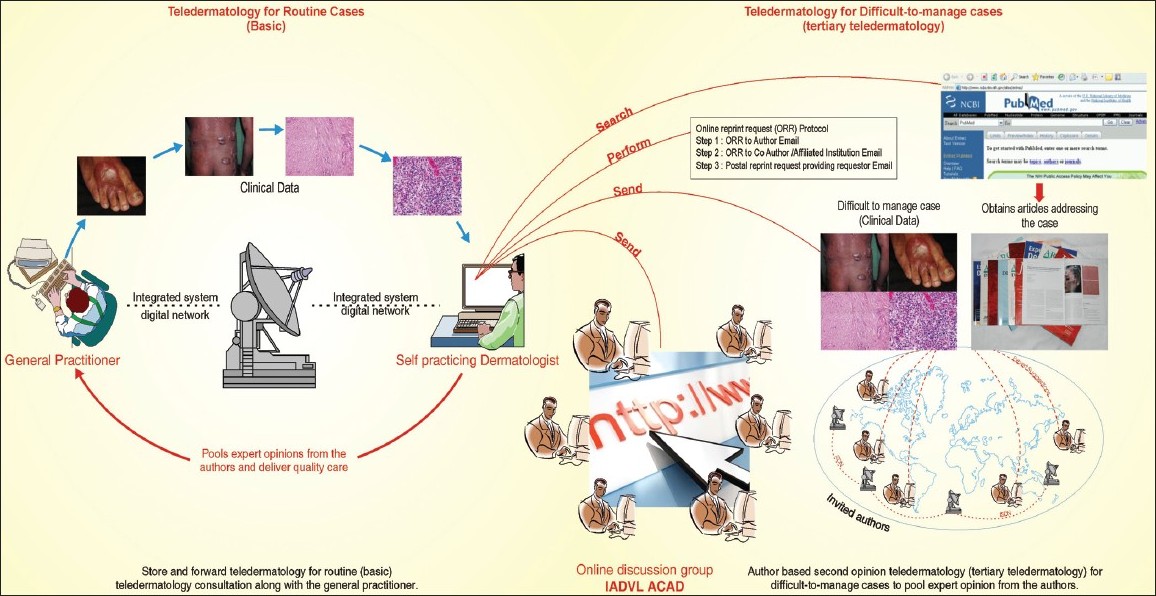
Teledermatology involves the diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions remotely using telemedicine applications. Patients can submit images or videos of their skin concerns, which dermatologists can review and provide recommendations for further management.
This approach improves access to specialized dermatological care, especially for individuals residing in areas with a shortage of dermatology clinics. Teledermatology offers a more efficient and timely method for managing various skin conditions.
Teleophthalmology

Teleophthalmology enables remote diagnosis and treatment of eye conditions. Through the use of digital retinal imaging and visual acuity testing, ophthalmologists can assess patients' eye health from a distance.
This allows for early identification of potential problems and prompt intervention. Teleophthalmology is particularly valuable in areas with limited access to specialized eye care, providing greater accessibility to quality eye healthcare services.
Challenges and Solutions
The path to success is filled with challenges. While developing a telemedicine application, chances are that healthcare organizations have to face a number of challenges. These challenges can be eliminated by following or adopting the practices mentioned below.
Technology and Infrastructure
Technology and infrastructure are major hurdles in offering efficient healthcare services. Institutions must be equipped with adequate internet connectivity so that the healthcare providers are available for the patients at all times. However, a steady internet might not be something patients from rural areas can still access.
Telemedicine applications can also come up with a few features that can be utilized by patients even without an internet connection. The application must also include data and privacy regulations to protect the sensitive information of both patients and healthcare providers from security breaches.
Licensure and Legal Issues
Since these applications are available in app stores globally, they are no longer restricted by geographical borders anymore. Patients from all across the world can utilize the services offered by telemedicine applications.
Due to this, the application should be developed in such a way that it should be in tune with the regulatory requirements of neighboring countries as well.
It is advised to consult a legal officer while developing applications to ensure that the application follows every necessary guideline and does not miss out on anything important.
Patient Acceptance and Adoption
Even after developing the telemedicine applications and serving them to your audience, they might still not go for it. Users might be skeptical of the application and refrain from using it.
Healthcare organizations are required to take the initiative to promote their applications among patients. Interactive sessions, campaigns, and advertisements can be launched to make users aware about the one-of-a-kind features present in your telemedicine application.
Future Trends in Telemedicine
Because of its scalability, telemedicine applications have the potential to survive in their full glory even in the near future. Here’s how:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Technological advancements have introduced new tools like Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These advancements can be easily utilized by healthcare organizations to enhance their existing telemedicine applications. AI can detect medical anomalies and identify potential emergencies.
ML algorithms can analyze large sets of patient data to provide personalized treatment plans and predict outcomes. Additionally, automation of administrative tasks can streamline healthcare processes, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care.
Wearable Technology and Remote Monitoring
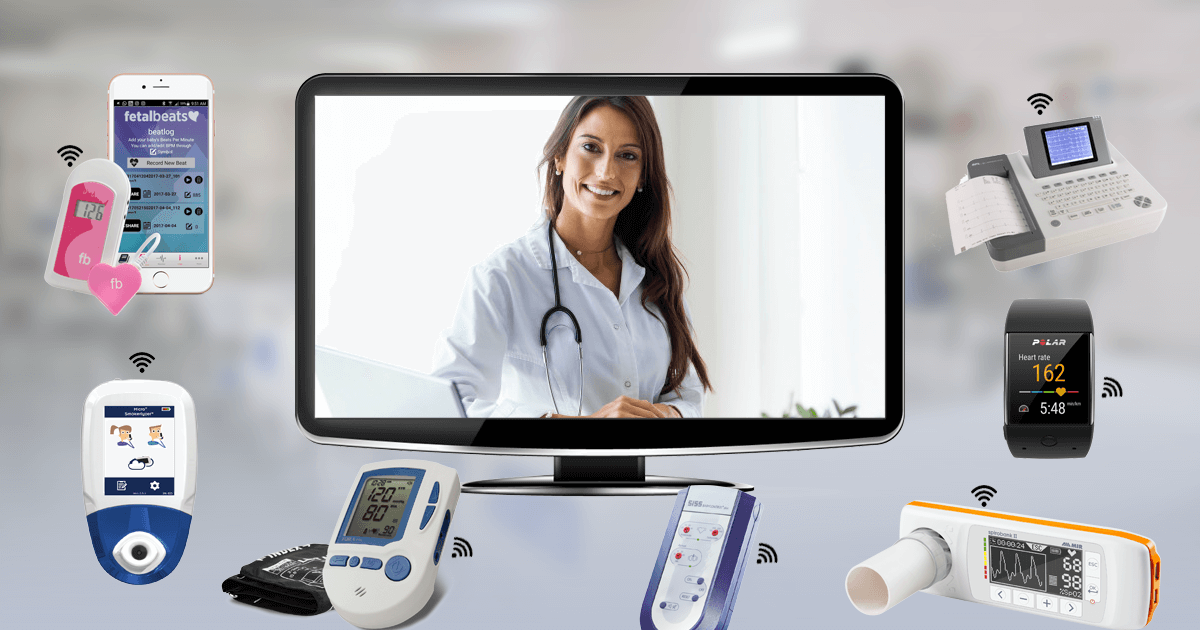

For patients with chronic conditions who are susceptible to major health issues, wearable technology and remote monitoring can be their best bet. Through this, their daily activities and vital signs can be tracked and directly sent to their healthcare provider.
The healthcare provider can now evaluate the information and provide them with medical aid accordingly. Remote monitoring ensures that the patient does not undergo serious health implications and ultimately leads to positive outcomes.
Virtual Reality and Telemedicine
Virtual reality (VR) offers exciting opportunities to enhance telemedicine experiences. VR-based therapy sessions and simulations can provide immersive environments for mental health interventions and rehabilitation programs.
Furthermore, VR can enable telepresence experiences for medical professionals, allowing them to collaborate and consult with colleagues from different locations. VR applications in telemedicine have the potential to improve patient engagement and outcomes.
Expansion of Telemedicine to Developing Countries
Telemedicine has the potential to bridge the healthcare access gap in developing countries. By leveraging mobile-based telemedicine solutions, healthcare services can reach underserved populations in remote areas.
Collaborations between telemedicine providers, non-profit organizations, and government initiatives can help ensure the availability of telemedicine infrastructure and resources in regions that lack sufficient healthcare facilities.
Conclusion
Telemedicine applications are transforming the healthcare landscape by providing convenient, cost-effective, and accessible healthcare solutions. Through teleconsultation, telepsychiatry, telecardiology, teledermatology, teleophthalmology, and other emerging fields, telemedicine is revolutionizing the way healthcare is delivered.
While challenges, such as technology limitations, legal complexities, and patient acceptance, need to be tackled, the future of telemedicine holds tremendous potential. Trends like AI and ML, wearable technology, VR applications, and expanding telemedicine to developing countries will further revolutionize healthcare accessibility and delivery.
It is crucial for providers, patients, and policymakers to embrace and integrate telemedicine to harness the full potential of this transformative technology in healthcare.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can telemedicine improve access to healthcare?
Telemedicine eliminates geographical barriers, making healthcare accessible to individuals in rural or underserved areas. Patients can connect with healthcare providers remotely, regardless of their location.
How does telemedicine reduce healthcare costs?
Telemedicine eliminates transportation expenses and reduces hospital readmissions, resulting in cost savings. Patients can access healthcare services remotely, saving money on travel and reducing unnecessary hospital visits.
In what ways does telemedicine enhance the patient experience?
Telemedicine reduces wait times, eliminates the need for long commutes, and enables convenient scheduling of virtual consultations. It also facilitates better communication between patients and healthcare professionals, leading to personalized care and higher patient satisfaction.
What fields of healthcare can telemedicine be applied to?
Telemedicine is utilized in various fields, including teleconsultation, telepsychiatry, telecardiology, teledermatology, and teleophthalmology. It enables remote diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of patients in these specialized areas.
What are the challenges for the future of telemedicine?
Telemedicine faces challenges such as technology and infrastructure limitations, licensure and legal issues, and patient acceptance and adoption. These challenges need to be addressed to fully harness the potential of telemedicine in healthcare.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Benefits of Telemedicine
- Telemedicine Applications in Different Fields
- Challenges and Solutions
- Future Trends in Telemedicine
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

